name: Update Your Online Security goal: Update password and personal data management. Create a backup, protect against hackers, and raise awareness about mass surveillance. objectives:
- Update on personal data management and tools that enhance your security.
- Implement a secure and user-friendly password manager.
- Implement two-factor authentication to strengthen security and minimize hacking risks.
A journey towards protecting your data
Welcome, everyone, to this educational program dedicated to digital security. This training is designed to be accessible to everyone, so no prior knowledge of computer science is required. Our primary goal is to equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate the digital world more safely and securely.
This will involve implementing several tools, including a secure email service, a password manager, and various software to enhance online security.
In this training, we are not aiming to make you an expert, anonymous, or invulnerable, as this is impossible. Instead, we offer you some simple and accessible solutions to start transforming your online habits and regain control of your digital sovereignty.
Contributors team: Muriel; design Rogzy Noury & Fabian; production Théo; contribution
Introduction
Course overview
Objective: Update your security skills !
Welcome, everyone, to this educational program dedicated to digital security. This training is designed to be accessible to everyone, so no prior knowledge of computer science is required. Our primary goal is to equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate the digital world more safely and securely.
This will involve implementing several tools, including a secure email service, a password manager, and various software to enhance online security.
This training is a collaborative effort of three of our professors:
- Renaud Lifchitz, cybersecurity expert
- Théo Pantamis, PhD in applied mathematics
- Rogzy, Co-founder of Plan ₿ Network
Your digital hygiene is crucial in an increasingly digital world. Despite the constant increase in hacking and mass surveillance, it is not too late to take the first step and protect yourself. In this training, we are not trying to make you an expert, anonymous, or invulnerable, as this is impossible. Instead, we offer you some simple and accessible solutions for everyone to start transforming your online habits and regain control of your digital sovereignty. If you are looking for more advanced skills on the subject, our resources, tutorials, or other cybersecurity training are here for you. In the meantime, here is a brief overview of our program for the next few hours together.
Section 1: Everything you need to know about online browsing
- Chapter 1 - Online Browsing
- Chapter 2 - Using the Internet Securely
To begin, we will discuss the importance of selecting a web browser and its associated security implications. We will then explore the specifics of browsers, particularly regarding cookie management. We will also see how to ensure a more secure and anonymous browsing experience, using tools such as TOR. Afterwards, we will focus on the use of VPNs to enhance the protection of your data. Finally, we will end with recommendations for the secure use of WiFi connections.

Section 2: Best practices for computer usage
- Chapter 3 - Computer usage
- Chapter 4 - Hacking & backup management
In this section, we will cover three key areas of computer security. First,
we will explore different operating systems, including Mac, PC, and Linux,
highlighting their specific characteristics and strengths. Next, we will
explore methods to effectively protect against hacking attempts and enhance
the security of your devices. Finally, we will emphasize the importance of
regularly safeguarding and backing up your data to prevent any loss or
ransomware. 
Section 3: Implementation of solutions
- Chapter 6 - Email management
- Chapter 7 - Password manager
- Chapter 8 - Two-factor authentication
In this practical third section, we will move on to the implementation of your concrete solutions.
First, we will see how to protect your email inbox, which is essential for
your communications and often targeted by hackers. Then, we will introduce
you to a password manager: a practical solution to prevent forgetting or
mixing up your passwords while keeping them secure. Finally, we will discuss
an additional security measure, two-factor authentication, which adds an
extra layer of protection to your accounts. Everything will be explained
clearly and accessibly. 
Ready to strengthen your digital security and take back control of your data? Let's go!
Everything you need to know about online browsing
Online browsing
When browsing the internet, it is essential to avoid common mistakes to maintain your online security. Here are some tips to avoid them:
Be cautious with software downloads:
It is recommended to download software from the official website of the
publisher rather than from generic sites. Example: Use www.signal.org/download instead of www.logicieltelechargement.fr/signal. 
It is also advisable to prioritize open-source software as they are often safer and free from malicious software. An "open-source" software is a type of software whose code is publicly available and accessible to everyone. This allows for verification, among other things, that there is no hidden access to steal your data.
Bonus: Open-source software is often free! This university is 100% open-source, so you can also review our code on GitHub.
Cookie management: Errors and best practices
Cookies are files created by websites to store information on your computer or mobile device. While some sites require these cookies to function properly, they can also be exploited by third-party sites, especially for advertising tracking purposes. Under regulations such as the GDPR, it is possible—and recommended—to refuse third-party tracking cookies while accepting those that are essential for the site's proper functioning. After each visit to a site, it is wise to delete the associated cookies, either manually or through an extension or a specific program. Some browsers even offer the possibility to delete cookies selectively. Despite these precautions, it is crucial to understand that the information collected by different sites can remain interconnected, hence the importance of finding a balance between convenience and security.
Note: Also, limit the number of extensions installed on your browser to avoid potential security and performance issues.
Web browsers: choices, security
There are two major families of browsers: those based on Chrome and those
based on Firefox. Although both families offer a similar level of security,
it is recommended to avoid using the Google Chrome browser due to its
tracking capabilities. Lighter alternatives to Chrome, such as Chromium or
Brave, may be preferred. Brave is particularly recommended for its built-in
ad blocker. It may be necessary to use multiple browsers to access certain
websites. 
Private browsing, TOR, and other alternatives for more secure and anonymous browsing
Private browsing, although it does not hide browsing from your internet service provider, allows you to avoid leaving local traces on your computer. Cookies are automatically deleted at the end of each session, allowing you to accept all cookies without being tracked. Private browsing can be useful when purchasing online services, as websites track our search habits and adjust prices accordingly. However, it is essential to note that private browsing is recommended for temporary and specific sessions, rather than for general internet browsing.
A more advanced alternative is the TOR (The Onion Router) network, which offers anonymity by masking the user's IP address and allowing access to the Darknet. TOR Browser is a browser specifically designed to use the TOR network. It enables you to visit both conventional websites and .onion websites, which are typically operated by individuals and may be associated with illegal activities.
TOR is a legal and widely used tool by journalists, freedom activists, and
others seeking to circumvent censorship in authoritarian countries. However,
it is important to understand that TOR does not secure the visited sites or
the computer itself. Additionally, using TOR can slow down the internet
connection as data passes through three other people's computers before
reaching its destination. It is also essential to note that TOR is not a
foolproof solution to guarantee 100% anonymity and should not be used for
illegal activities. 
VPN and internet connection
VPNs
Protecting your internet connection is a crucial aspect of online security, and using virtual private networks (VPNs) is an effective method to enhance this security, both for businesses and individual users.
VPNs are tools that encrypt data transmitted over the internet, making the
connection more secure. In a professional context, VPNs enable employees to
securely access the company's internal network from remote locations. The
exchanged data is encrypted, making it much more difficult for third parties
to intercept. In addition to securing access to an internal network, using a
VPN can allow a user to route their internet connection through the
company's internal network, giving the impression that their connection is
coming from the company. This can be particularly useful for accessing
online services that are geographically restricted. 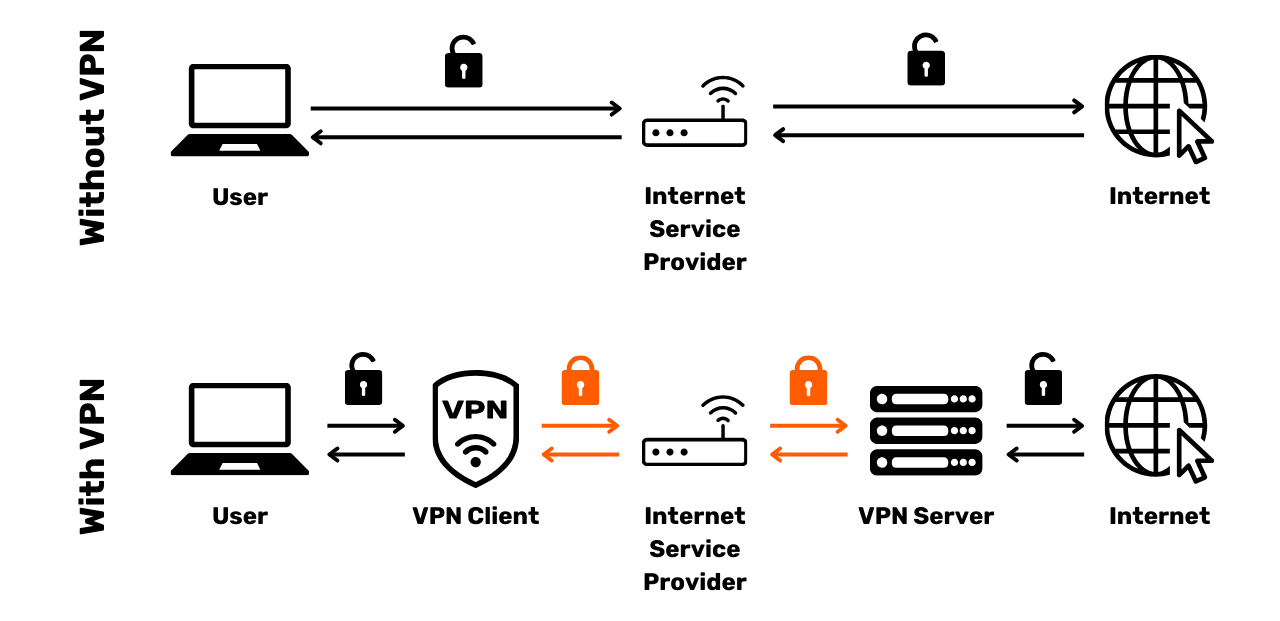
Types of VPNs
There are two primary types of VPNs: enterprise VPNs and consumer VPNs, such as Nordvpn. Enterprise VPNs tend to be more expensive and complex, whereas consumer VPNs are generally more accessible and user-friendly. For example, NordVPN enables users to connect to the internet through a server located in another country, thereby bypassing geographical restrictions.
However, using a consumer VPN does not guarantee complete anonymity. Many
VPN providers retain information about their users, which could compromise
their anonymity. Although VPNs can be useful for improving online security,
they are not a universal solution. They are effective for specific uses,
such as accessing geographically limited services or enhancing security
while travelling, but they do not guarantee total security. When selecting a
VPN, it is crucial to prioritize reliability and technical expertise over
popularity. VPN providers that collect the least personal information are
generally the safest. Services like iVPN and Mullvad do not collect personal
information and even allow payments in Bitcoin for increased privacy.  Finally, a VPN can also be used to block online advertisements, providing a more
enjoyable and secure browsing experience. However, it is essential to conduct
thorough research to find the VPN that best suits your needs. Using a VPN is
recommended to enhance security, even when browsing the internet at home. This
helps ensure a higher level of protection for exchanged data online. Finally,
could you check the URLs and the small padlock in the address bar to confirm
that you are on the intended site?
Finally, a VPN can also be used to block online advertisements, providing a more
enjoyable and secure browsing experience. However, it is essential to conduct
thorough research to find the VPN that best suits your needs. Using a VPN is
recommended to enhance security, even when browsing the internet at home. This
helps ensure a higher level of protection for exchanged data online. Finally,
could you check the URLs and the small padlock in the address bar to confirm
that you are on the intended site?
HTTPS & public Wi-Fi networks
In terms of online security, it is essential to understand that 4G is generally more secure than public Wi-Fi. However, using 4G can quickly deplete your mobile data plan. The HTTPS protocol has become the standard for encrypting data on websites. It ensures that the data exchanged between the user and the website is secure. Therefore, it is essential to verify that the site you are visiting uses the HTTPS protocol.
In the European Union, data protection is regulated by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Therefore, it is safer to use European Wi-Fi access point providers, such as SNCF, which do not resell user connection data. However, the mere fact that a site displays a padlock does not guarantee its authenticity. It is important to verify the site's public key using a certificate system to confirm its authenticity. Although data encryption prevents third parties from intercepting exchanged data, it is still possible for a malicious individual to impersonate the site and transfer data in plain text.
To avoid online scams, it is crucial to verify the identity of the site you
are browsing, especially by checking the extension and domain name.
Additionally, be vigilant against scammers who use similar letters in URLs
to deceive users. 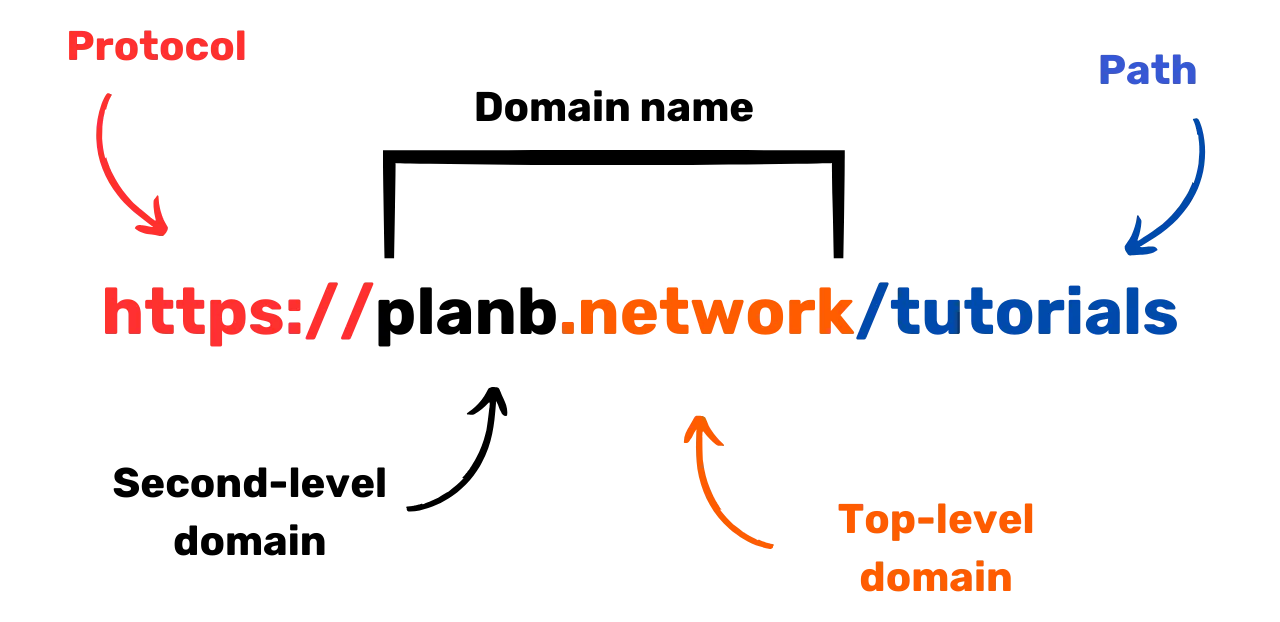 In summary, the use of a VPN can greatly improve online security for both businesses
and individual users. Furthermore, practising good browsing habits can contribute
to better digital hygiene. In the next segment of this course, we will cover
computer security, including updates, antivirus software, and password management.
In summary, the use of a VPN can greatly improve online security for both businesses
and individual users. Furthermore, practising good browsing habits can contribute
to better digital hygiene. In the next segment of this course, we will cover
computer security, including updates, antivirus software, and password management.
Best Practices for Computer Use
Computer Use
The security of our computers is a major concern in today's digital world. Today, we will address three key points:
- Choosing the computer
- Updates and antivirus for optimal security
- Best practices for the security of your computer and data.
Choosing the Computer and Operating System
Regarding the choice of the computer, there is no significant difference in
security between old and new computers. However, security differences exist
among operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and Mac.  Regarding Windows, it is recommended not to use an administrator account daily,
but rather to create two separate accounts: one for administrator use and another
for daily use. Windows is often more vulnerable to malware due to its large number
of users and the ease of switching from a standard user to an administrator.
On the other hand, threats are less common on Linux and Mac.
Regarding Windows, it is recommended not to use an administrator account daily,
but rather to create two separate accounts: one for administrator use and another
for daily use. Windows is often more vulnerable to malware due to its large number
of users and the ease of switching from a standard user to an administrator.
On the other hand, threats are less common on Linux and Mac.
The choice of operating system should be based on your needs and
preferences. Linux systems have evolved significantly in recent years,
becoming increasingly user-friendly. Ubuntu is an interesting alternative
for beginners, with an easy-to-use graphical interface. It is possible to
partition a computer to experiment with Linux while keeping Windows, but
this can be a complex process. It is often preferable to have a dedicated
computer, a virtual machine, or a USB key to test Linux or Ubuntu. 
Software Updates
Regarding updates, the rule is simple: Regularly updating the operating system and applications is essential.
On Windows 10, updates are almost continuous, and it is crucial not to block or delay them. Each year, approximately 15,000 vulnerabilities are identified, underscoring the importance of keeping software up to date to protect against malware and other cyber threats. Generally, software support ends between 3 and 5 years after its release, so it is necessary to upgrade to a higher version to continue benefiting from security updates.
The rule applies to almost all software. Indeed, updates are not intended to make your machine obsolete or slow; rather, they are designed to protect it from new threats. Some updates are even considered major, and without them, your computer is at serious risk of exploitation.
To provide a concrete example of an error, cracked software that cannot be updated poses a double potential threat. The arrival of a virus during its illegal download from a suspicious website and an insecure use against new forms of attack.
Anti-virus
- Do you need an antivirus? YES
- Do you have to pay? It depends!
The choice and implementation of an anti-virus is important. Windows
Defender, the built-in antivirus in Windows, is a safe and effective
solution. For a free solution, it is extremely good and much better than
many free solutions found online. Indeed, caution should be exercised when
downloading antivirus software from the Internet, as it may be malicious or
outdated. For those who wish to invest in a paid antivirus, it is
recommended to choose an antivirus that intelligently analyzes unknown and
emerging threats, such as Kaspersky. Antivirus updates are crucial for
protecting against emerging threats. 
Note: Linux and Mac, thanks to their user rights separation system, often do not need antivirus.
Finally, here are some best practices for securing your computer and data. It is important to choose an effective and user-friendly antivirus. It is also crucial to adopt good practices on your computer, such as not inserting unknown or suspicious USB keys. These USB keys may contain malicious programs that can automatically launch upon insertion. Checking the USB key will be useless once it has been inserted. Some companies have been victims of hacking due to USB keys being carelessly left in accessible areas, such as parking lots.
Treat your computer as you would your home: stay vigilant, regularly update your software, delete unnecessary files, and use a strong password for added security. It is crucial to encrypt data on laptops and smartphones to prevent theft or data loss. BitLocker for Windows, LUKS for Linux, and the built-in option for Mac are solutions for data encryption. It is recommended to activate data encryption without hesitation and to write down the password on paper to be kept in a safe place.
In conclusion, it is essential to choose an operating system that suits your needs and regularly update it, as well as the installed applications. It is also crucial to utilise an effective and user-friendly antivirus program and adopt good security practices to protect your computer and data.
Hacking & Backup Management: Protecting Your Data
How do hackers attack?
To protect yourself effectively, it is essential to understand how hackers attempt to infiltrate your computer. Indeed, viruses do not often appear magically, but rather are the consequences of our actions, even if unintentional.
As a general rule, viruses arrive because you have allowed your computer to invite them into your home. This can be visualized by downloading suspicious software, a compromised torrent file, or simply by clicking on the link in a fraudulent email.
Phishing, vigilance against fraudulent emails:
Attention! Emails are the first vector of attack. Here are some tips:
- Stay alert to phishing attempts that aim to extract sensitive information, such as your credentials and passwords. Avoid clicking on suspicious links and sharing your personal information without verifying the sender's legitimacy.
- Be cautious with email attachments and images: Email attachments and images can contain malware. Do not download or open attachments from unknown or suspicious senders, and ensure your antivirus software is up to date.
The golden rule here is to carefully check the full name of the sender as well as the origin of the email. When in doubt, delete it!
Ransomware and types of cyber attacks:
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts user data and
demands a ransom to decrypt it. This type of attack is becoming increasingly
common and can be very troublesome for both companies and individuals. To
protect yourself, it is imperative to create backups of the most sensitive
files! This will not stop the ransomware, but it will allow you to ignore
it. 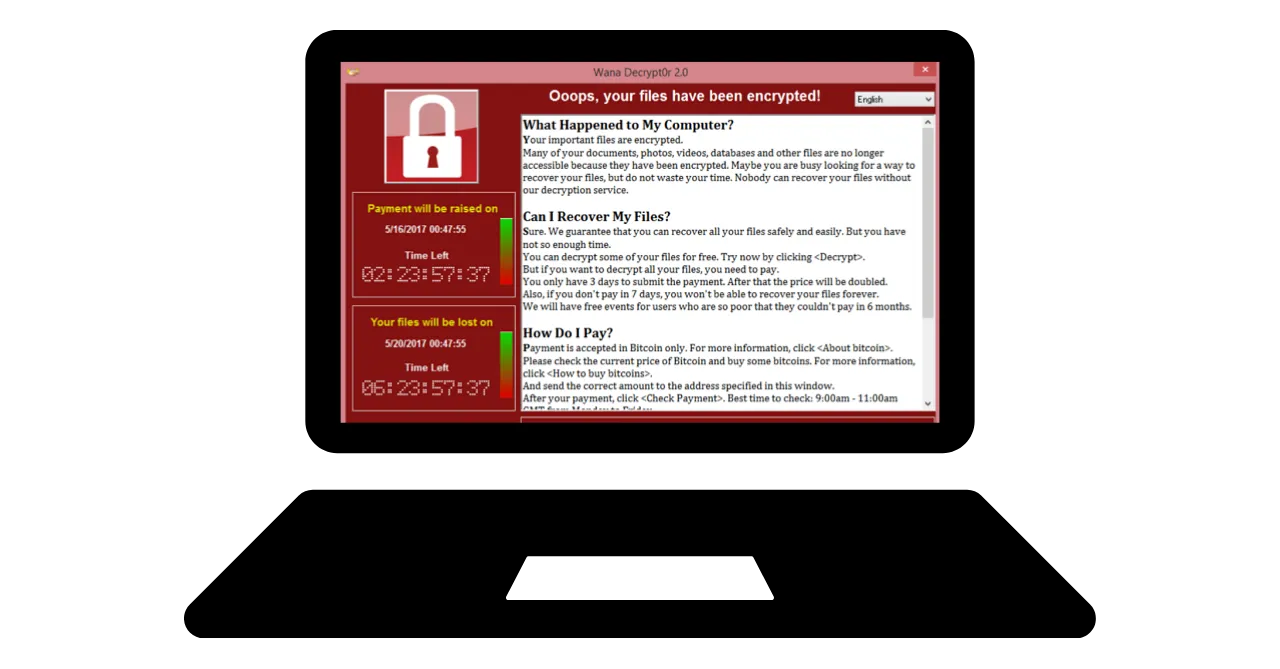 Regularly back up your important data to an external storage device or a secure
online storage service. This way, in the event of a cyber attack or hardware
failure, you can recover your data without losing crucial information.
Regularly back up your important data to an external storage device or a secure
online storage service. This way, in the event of a cyber attack or hardware
failure, you can recover your data without losing crucial information.
Simple solution:
Purchase an external hard drive and copy your data onto it. Disconnect it and store it in a safe location within the house. (Doing this twice and storing one of the drives in another location helps protect against potential fire.)
Create a cloud backup using ProtonMail Drive, Sync, or Google Drive. Upload your sensitive data to this online host. However, be aware that your data is potentially on the internet and held by a trusted third party.
Should you pay the hackers?
NO, it is generally not recommended to pay hackers in the case of ransomware or other types of attacks. Paying the ransom does not guarantee the recovery of your data and can encourage cybercriminals to continue their malicious activities. Instead, prioritize prevention and regular data backups to protect yourself.
If you detect a virus on your computer, disconnect it from the internet, perform a full antivirus scan, and delete infected files. Then, update your software and operating system, and change your passwords to prevent further intrusions.
Implementation of solutions.
Managing email accounts
Setting up a new email account!
The email account is the central point of your online activity: if it is compromised, a hacker can use it to reset all your passwords via the "forgot password" function and gain access to many other sites. That's why you need to secure it properly.
An email account should be created with a unique and strong password (details in chapter 7) and ideally with a two-factor authentication system (details in chapter 8).
Although we all already have an email account, it's essential to consider creating a new, more modern one to start fresh.
Choosing an email provider and managing email addresses
Proper management of our email addresses is crucial to ensure the security
of our online access. It is important to choose a secure and
privacy-respecting email provider. For example, ProtonMail is a safe and
privacy-respecting email service.  When choosing an email provider and creating a password, it is essential to never
reuse the same password for different online services. It is recommended to regularly
create new email addresses and use them for various purposes. It is advisable
to use a secure email service for critical accounts. It is also worth noting
that some services limit the length of passwords, so it is essential to be aware
of this limitation. Services are also available for creating temporary email
addresses, which can be used for accounts with a limited duration.
When choosing an email provider and creating a password, it is essential to never
reuse the same password for different online services. It is recommended to regularly
create new email addresses and use them for various purposes. It is advisable
to use a secure email service for critical accounts. It is also worth noting
that some services limit the length of passwords, so it is essential to be aware
of this limitation. Services are also available for creating temporary email
addresses, which can be used for accounts with a limited duration.
Just to let you know, older email providers, such as La Poste, Arobase, Wig, and Hotmail, are still in use, but their security practices may not be as robust as those of Gmail. Therefore, it is recommended to have two separate email addresses: one for general communications and the other for account recovery, with the latter being more secure. It is best to avoid mixing your email address with that of your phone operator or internet service provider, as this can serve as an attack vector.
Should I change my email account?
You should use the Have I Been Pwned website (https://haveibeenpwned.com/) to check if your email address has been compromised and to receive
notifications of future data breaches. Hackers can exploit a hacked database
to send phishing emails or reuse compromised passwords. 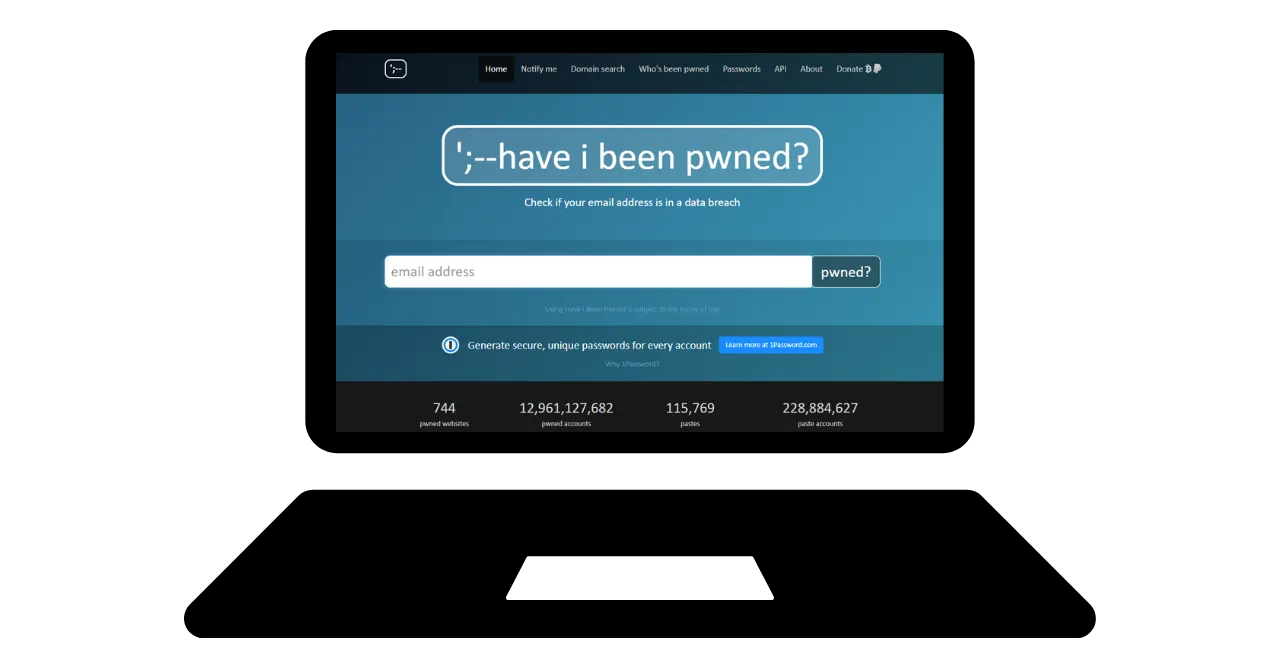 In general, starting to use a new, more secure email address is not a bad practice
and is even necessary if one wants to start fresh on a healthy basis. Bonus Bitcoin:
It may be advisable to create a specific email address for our Bitcoin activities,
such as creating exchange accounts, to separate these areas of activity in our
lives truly.
In general, starting to use a new, more secure email address is not a bad practice
and is even necessary if one wants to start fresh on a healthy basis. Bonus Bitcoin:
It may be advisable to create a specific email address for our Bitcoin activities,
such as creating exchange accounts, to separate these areas of activity in our
lives truly.
Password Manager
What is a password manager?
A password manager is a tool that enables you to store, generate, and manage passwords for various online accounts. Instead of remembering multiple passwords, you only need one master password to access all the others.
With a password manager, you no longer have to worry about forgetting your passwords or writing them down somewhere. You only need to remember one master password. Additionally, most of these tools generate strong passwords for you, which enhances the security of your accounts.
Differences between some popular managers:
LastPass: One of the most popular managers. It is a third-party service, which means your passwords are stored on their servers. It offers both a free and a paid version, featuring a user-friendly interface.
Dashlane: It is also a third-party service, with an intuitive interface and additional features such as tracking credit card information and secure notes.

Self-hosting for more control:
Bitwarden: It is an open-source tool, which means you can review its code to verify its security. Although Bitwarden offers a hosted service, it also allows users to self-host, which means you can control where your passwords are stored, potentially offering more security and control.
KeePass: It is an open-source solution that is primarily intended for self-hosting. Your data is stored locally by default, but you can synchronize the password database using different methods if you wish. KeePass is widely recognized for its security and flexibility, although it may be slightly less user-friendly for beginners.
 (Note: Choosing between a third-party service or a self-hosted service depends
on your level of technological comfort and how you prioritize control versus
convenience. Third-party services are generally more convenient for most
people, while self-hosting requires more technical knowledge but can offer
more control and peace of mind in terms of security.)
(Note: Choosing between a third-party service or a self-hosted service depends
on your level of technological comfort and how you prioritize control versus
convenience. Third-party services are generally more convenient for most
people, while self-hosting requires more technical knowledge but can offer
more control and peace of mind in terms of security.)
What makes a good password:
A good password is generally:
- Long: at least 12 characters.
- Complex: a mixture of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Unique: do not reuse the same password for different accounts.
- Not based on personal information: avoid birth dates, names, etc.
To ensure the security of your account, it is crucial to create strong and secure passwords. The length of the password is not enough to ensure its security. The characters must be completely random to resist brute force attacks. The independence of events is also important to avoid the most likely combinations. Common passwords such as "password" are easily compromised.
To create a strong password, it is recommended to use a large number of random characters, without using predictable words or patterns. It is also essential to include numbers and special characters. However, it is worth noting that some websites may restrict the use of certain special characters. Passwords that are not randomly generated are easy to guess. Variations or additions to passwords are not secure. Websites cannot guarantee the security of passwords chosen by users.
Randomly generated passwords offer a higher level of security, although they may be more difficult to remember. Password managers can develop more secure random passwords. By using a password manager, you don't need to memorize all your passwords. It is essential to gradually replace your old passwords with those generated by the manager, as they are stronger and more secure. Ensure that the master password of your password manager is also strong and safe.
Two-Factor Authentication
Why implement 2FA
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is an additional layer of security that ensures the person attempting to access an online account is who they claim to be. Instead of just entering a username and password, 2FA requires an additional form of verification.
This second step can be:
- A temporary code sent via SMS.
- A code generated by an application like Google Authenticator or Authy.
- A physical security key that you insert into your computer.
 With 2FA, even if a hacker obtains your password, they will still be unable
to access your account without this second verification factor. This makes
2FA essential for protecting your online accounts against unauthorized access.
With 2FA, even if a hacker obtains your password, they will still be unable
to access your account without this second verification factor. This makes
2FA essential for protecting your online accounts against unauthorized access.
Which option to choose?
The various options for strong authentication provide different levels of security.
- SMS is not considered the best option as it only provides proof of possession of a phone number.
- 2FA (two-factor authentication) is more secure as it uses multiple types of evidence, such as knowledge, possession, and identification. One-time passwords (HOTP and TOTP) are safer than SMS because they require cryptographic calculation and are stored locally rather than in memory.
- Hardware tokens, such as USB keys or smart cards, offer optimal security by generating a unique private key for each site and verifying the URL before allowing the connection.
For optimal security with strong authentication, it is recommended to use a secure email address, a secure password manager, and adopt 2FA using YubiKeys. It is also advisable to purchase two YubiKeys to anticipate loss or theft, for example, keeping a backup copy both at home and on your person.
As for potential threats to SIM 2FA, a common example is a SIM swap attack, where an attacker steals a user's phone number by linking it to a SIM card controlled by the attacker, there are several ways an attacker can complete the attack; however, this threat is usually only a major concern for high-profile individuals and people of interest.
Biometrics can be used as a substitute, but it is less secure than the combination of knowledge and possession. Biometric data should be stored on the authentication device and not disclosed online. It is important to consider the threat model associated with different authentication methods and adjust practices accordingly.
Finally, it may be useful to provide a brief context about HOTP and TOTP OTPs: HOTP is a one-time password based on the HMAC (Hash-based Message Authentication Code) algorithm, while TOTP is a time-based OTP. Key features of such algorithms are that passwords can only be used once, each generated value is unique, and a shared key exists between the user's device (client) and the authentication service (server). The primary difference between the two systems lies in how the factor is generated: the TOTP is time-based, whereas the HOTP system is counter-based.
Conclusion of the training:
As you have understood, implementing good digital hygiene is not necessarily simple, but it remains accessible!
- Creating a new secure email address.
- Setting up a password manager.
- Activating 2FA.
- Gradually replacing our old passwords with strong passwords with 2FA.
Keep learning and gradually implement good practices!
Golden rule: Cybersecurity is a moving target that will adapt to your learning journey!
Practical Section
Setting up a Mailbox
Protecting your email account is a crucial step in securing your online activities and safeguarding your data. This tutorial will guide you, step by step, in creating and setting up a ProtonMail account, a provider known for its high level of security that offers end-to-end encryption of your communications. Whether you are a novice or an experienced user, the best practices presented here will help you strengthen the security of your email while taking advantage of ProtonMail's advanced features:
Securing in 2FA
Two-factor authentication (2FA) has become essential for securing your online accounts. In this tutorial, you will learn how to set up and use the 2FA app Authy, which generates dynamic 6-digit codes to protect your accounts. Authy is very easy to use and synchronizes across multiple devices. Discover how to install and configure Authy, and thus strengthen the security of your online accounts right now:
Another option is to use a physical security key. This additional tutorial shows you how to set up and use a security key as a second authentication factor:
Creating a password manager
Password management is a challenge in the digital age. We all have numerous online accounts to secure. A password manager helps you create and store strong and unique passwords for each account.
In this tutorial, learn how to set up Bitwarden, an open-source password manager, and how to sync your credentials across all your devices to simplify your daily use:
For more advanced users, I also offer a tutorial on another free and open-source software to use locally for managing your passwords:
Securing your accounts
In these two tutorials, I also guide you in securing your online accounts and explain how to gradually adopt more secure practices for managing your passwords daily.
Back-up set-up
Protecting your files is also a crucial point. This tutorial shows you how to implement an effective backup strategy using Proton Drive. Discover how to use this secure cloud solution to apply the 3-2-1 method: three copies of your data on two different media, with one copy offsite. This ensures the accessibility and security of your sensitive files:
And to secure your files stored on removable media like a USB drive or external hard drive, I also show you how to encrypt and decrypt these media using VeraCrypt easily:
Change of browser & VPN
Protecting your online privacy is also a crucial point to ensure your security. Using a VPN can be a first solution to achieve this.
I suggest exploring two reliable VPN solutions that accept Bitcoin payments, namely IVPN and Mullvad. These tutorials guide you on how to install, configure, and use Mullvad or IVPN on all your devices:
Also, learn how to use Tor Browser, a browser specifically designed to protect your online privacy:
Go further
How to work in the cybersecurity industry
Cybersecurity: A Growing Field with Endless Opportunities
If you are passionate about protecting systems and data, the field of cybersecurity offers numerous opportunities. If this industry intrigues you, here are some key steps to guide you.
Academic Foundations and Certifications:
A solid education in computer science, information systems, or a related field is often the ideal starting point. These studies provide the necessary foundation to understand the technical challenges of cybersecurity. To complement this education, it is wise to obtain recognized certifications in the field. While these certifications may vary by region, some, such as CISSP or CEH, enjoy global recognition.
Cybersecurity is a vast and constantly evolving field. Familiarizing yourself with essential tools and different systems is crucial. Additionally, with numerous subdomains, ranging from incident response to ethical hacking, it is beneficial to identify your niche and specialize in it.
Gaining Practical Experience:
The importance of practical experience cannot be underestimated. Seeking internships or junior positions in companies with cybersecurity teams is an excellent way to apply your theoretical knowledge and gain practical experience. Furthermore, engaging in ethical hacking competitions or cybersecurity simulations can refine your skills in real-world situations.
The strength of a professional network is invaluable. Joining professional associations, hackerspaces, or online forums provides a platform to exchange ideas with other experts. Similarly, attending cybersecurity conferences and workshops not only allows you to learn but also helps you build connections with industry professionals.
The constant evolution of threats requires regular monitoring of news and specialized forums. In a sector where trust is paramount, acting with ethics and integrity is essential at every stage of your career.
Skills and Tools to Deepen:
- Cybersecurity Tools: Wireshark, Metasploit, Nmap.
- Operating Systems: Linux, Windows, MacOS.
- Programming Languages: Python, C, Java.
- Networks: TCP/IP, VPN, firewall.
- Databases: SQL, NoSQL.
- Cryptography: SSL/TLS, symmetric and asymmetric encryption.
- Incident Management: Log analysis, incident response.
- Ethical Hacking: Penetration testing techniques and intrusion testing.
- Governance: ISO standards, GDPR, and CCPA regulations.
By mastering these skills and tools, you will be well-equipped to navigate
the world of cybersecurity successfully. 
Interview with Renaud
Efficient Password Management and Authentication Strengthening: An Academic Approach
Three are key dimensions to consider when talking about password managers: the creation, updating, and implementation of passwords on websites.
It is generally not recommended to use browser extensions for automatic password filling. These tools can make the user more vulnerable to phishing attacks. Renaud, a recognized expert in cybersecurity, prefers manual management using KeePass, which involves manually copying and pasting passwords into the application. Extensions tend to increase the attack surface, can slow down browser performance, and therefore present a significant risk. Thus, minimising the use of extensions on the browser is a recommended practice.
Password managers generally encourage the use of additional authentication
factors, such as two-factor authentication. For optimal security, it is
advisable to keep OTPs (One-Time Passwords) on your mobile device. AndOTP
provides an open-source solution for generating and storing one-time
password (OTP) codes on your mobile device. While Google Authenticator
allows exporting authentication code seeds, trust in backup on a Google
account remains limited. Therefore, the OTI and AndoTP applications are
recommended for autonomous OTP management.  The question of digital inheritance and digital mourning highlights the importance
of having a procedure in place to transmit passwords after a person's death.
A password manager facilitates this transition by securely storing all digital
secrets in one place. The password manager also allows you to identify all open
accounts and manage their closure or transfer. It is recommended to write down
the master password on paper, but it should be kept in a concealed and secure
location. If the hard drive is encrypted and the computer is locked, the password
will not be accessible, even in the case of burglary.
The question of digital inheritance and digital mourning highlights the importance
of having a procedure in place to transmit passwords after a person's death.
A password manager facilitates this transition by securely storing all digital
secrets in one place. The password manager also allows you to identify all open
accounts and manage their closure or transfer. It is recommended to write down
the master password on paper, but it should be kept in a concealed and secure
location. If the hard drive is encrypted and the computer is locked, the password
will not be accessible, even in the case of burglary.
Towards a Post-Password Era: Exploring Credible Alternatives
Passwords, although ubiquitous, have several disadvantages, including the risk of transmission during the authentication process. Leading companies, such as Microsoft and Apple, offer innovative alternatives, including biometrics and hardware tokens, indicating a progressive trend toward abandoning passwords.
Passkeys, for example, offer encrypted random keys combined with a local factor (such as biometrics or a PIN), which a provider hosts but remains out of their reach. Although this requires updating websites, the approach eliminates the need for passwords, thus providing a high level of security without the constraints associated with traditional passwords or the issue of managing a digital safe.
Passkiz is another viable and secure alternative for password management. However, a major question remains: the availability in case of provider failure. It would therefore be desirable for internet giants to propose systems to guarantee this availability.
Direct authentication to the relevant service is a viable option that eliminates the need for a third party. However, the Single Sign-On (SSO) offered by internet giants also poses problems in terms of availability and risks of censorship. To prevent data leaks, it is crucial to minimize the amount of information collected during the authentication process.
Computer security: imperatives of safe practices and risks related to human negligence
Computer security can be compromised by simple practices and the use of default passwords, such as "admin". Sophisticated attacks are not always necessary to jeopardize computer security. For example, the administrator passwords of a YouTube channel were written in a company's private source code. Security vulnerabilities are often the result of human negligence.
It is also worth noting that the Internet is highly centralized and largely under American control. The DNS server can be subject to censorship and often employs deceptive DNS to block access to certain sites. DNS is an outdated and insecure protocol that can lead to security issues. New protocols, such as DNSsec, have emerged but are still not widely used. To bypass censorship and ad blocking, it is possible to choose alternative DNS providers.'
Alternatives to intrusive advertisements include Google DNS, OpenDNS, and other independent services. The standard DNS protocol leaves DNS queries visible to the Internet service provider. DOH (DNS over HTTPS) and DOT (DNS over TLS) encrypt the DNS connection, providing greater privacy and security. These protocols are widely used in enterprises due to their enhanced security and are natively supported by Windows, Android, and iPhone. To use DOH and DOT, a TLS hostname must be entered instead of an IP address. Free DOH and DOT providers are available online. DOH and DOT improve privacy and security by avoiding "man-in-the-middle" attacks.
It is also worth mentioning the system called "Lightning authentication", which generates a different identifier for each service, without the need to provide an email address or personal information. It is possible to have user-controlled decentralized identities, but there is a lack of standardization and normalization in decentralized identity projects. Package managers such as NuGet and Chocolaté, which allow downloading open-source software outside of the Microsoft Store, are recommended to avoid malicious attacks. In summary, DNS is crucial for online security; however, it is essential to remain vigilant against potential attacks on DNS servers.
Final Section
Reviews & Ratings
6be74d2d-2116-5386-9d92-c4c3e2103c68 true
Final Exam
a894b251-a85a-5fa4-bf2a-c2a876939b49 true
Conclusion
6270ea6b-7694-4ecf-b026-42878bfc318f true