name: The Bitcoin Journey goal: Discover Bitcoin fundamentals, including its monetary value proposition, miners, transactions, and wallets. objectives:
- Gain a general understanding of the Bitcoin technology
- Understand how to buy and secure bitcoins
- Have a general understanding of the Blockchain technology
- Familiarize with the concept of Lightning Network
- Realize the geopolitical and social impact of Bitcoin
Your First Bitcoin Adventure
In this course, we will explain the basics of Bitcoin in 25 chapters, so that you can understand this technology in a simple and effective way. The course explores the basics of the industry as a whole, including topics like mining, wallets, buying/selling platforms, and more. Additional educational material will be available throughout the journey, and we also invite you to check the "21 Posters" in the resources section after you finish this course.
You don't need any specific knowledge to get started. In fact, the following content is accessible to students of all levels, and it should take approximately 15 hours to finish.
Introduction
Course overview
Welcome to the BTC101 course!
Bitcoin is a technological and a monetary revolution, capable of making us question our relationship with money and society. In fact, Bitcoin (referred to as BTC) is a neutral and decentralized currency, which means that it is not controlled by any entity or institution. It is an innovation that goes beyond a mere "internet currency": it is both a computer protocol (Bitcoin) and a monetary unit (bitcoin).
The Bitcoin protocol uses underlying technologies such as cryptography, network communication, and the famous "blockchain", while the bitcoin unit serves as the necessary currency for the proper functioning of this protocol. In everyday life, Salvadorians and bitcoiners around the world use the bitcoin currency to buy and sell goods and services, relying on this technology to make their lives better.
A comprehensive yet accessible curriculum:
In this course, we will discuss some monetary aspects of Bitcoin, including how to buy and sell bitcoins, securely store them in digital wallets, and use them for transactions. We will also examine the role of miners, who are essential for creating new bitcoins and securing the Bitcoin network. Finally, we will explore the future of Bitcoin and how the Lightning Network technology can improve Bitcoin transactions.

It is essential to understand that Bitcoin is a new monetary system that completely changes our relationship with money, so learning how to use it is a necessary skill for anyone who wants to be in control of their own funds.
Section 1 - Introduction
- Chapter 1 - Course Overview
- Chapter 2 - The Prehistory of Bitcoin
Section 2 - Money
- Chapter 3 - Money Throughout History
- Chapter 4 - Fiat Currencies
- Chapter 5 - Hyperinflation
- Chapter 6 - 21 Million Bitcoins
Section 3 - Bitcoin Wallets
- Chapter 7 - What is a Bitcoin Wallet?
- Chapter 8 - Bitcoin Wallets and Security
- Chapter 9 - Setting Up a Wallet
- Chapter 10 - Standing the Test of Time
Section 4 - The Technical Aspects of Bitcoin
- Chapter 11 - Launching Bitcoin
- Chapter 12 - Bitcoin Transactions
- Chapter 13 - Bitcoin Nodes
- Chapter 14 - Miners
- Chapter 15 - Bitcoin and Ecology
Section 5 - How to Obtain Bitcoins?
- Chapter 16 - Bitcoin Never Sleeps!
- Chapter 17 - Earning Bitcoins Through Work
- Chapter 18 - Saving with Bitcoin
- Chapter 19 - Hyperbitcoinization
Section 6 - The Future of Bitcoin: The Lightning Network
- Chapter 20 - A Brief Introduction to the Lightning Network
- Chapter 21 - Lightning Network Use Cases
- Chapter 22 - Red Pill or Blue Pill?
Before introducing the definition of money and its function in society (Chapter 1), we should start from the genesis of Bitcoin. Launched in 2009, Bitcoin is a relatively new technology unlike anything else. It is therefore normal not to understand everything about it, all at once. In fact, just like when learning how to use the Internet or to drive a car, you don’t need to know all the technical details right away: you can start by learning how to receive, pay, and secure your funds, and then take small steps to study it more deeply.
After all, we are only at the beginning stages of its adoption, as we have passed the takeoff phase: you are just in time to acquire as much knowledge as you wish regarding this important innovation.
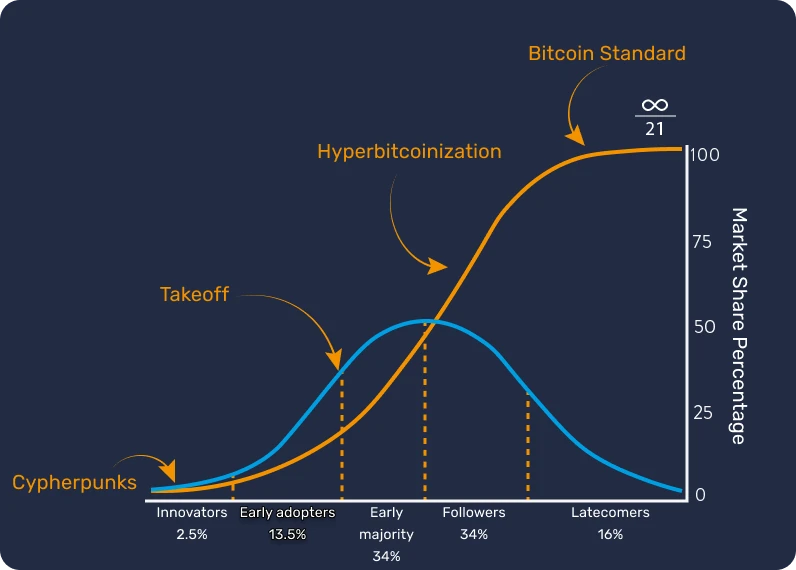
The important point here is to understand this new technology in a general way, so we hope you enjoy this course and continue to make progress in this new global monetary paradigm.
Ready to dive into the fascinating world of Bitcoin and understand all its inner workings? Let's go!
The Prehistory of Bitcoin
Before the term "Bitcoin" became synonymous with digital currency and financial transformation, the groundwork for its creation was laid by a series of ideas, innovations, and social movements. Among these, the cypherpunk movement stands out as a key element in the prehistory of Bitcoin.
Cypherpunks: visionaries of the digital world
 In the heart of the technological evolution of the 1980s and 1990s, a group of
people began to deeply question the role of privacy and freedom in the digital
age. These individuals, who would later be known as "cypherpunks", firmly believed
that cryptography could serve as a tool to protect individual rights against
the interference from governments and large corporations.
In the heart of the technological evolution of the 1980s and 1990s, a group of
people began to deeply question the role of privacy and freedom in the digital
age. These individuals, who would later be known as "cypherpunks", firmly believed
that cryptography could serve as a tool to protect individual rights against
the interference from governments and large corporations.
Iconic figures such as Julian Assange, Wei Dai, Tim May, and David Chaum played a pivotal role in shaping the philosophy and vision of the movement. These thinkers shared their ideas on an influential mailing list, where participants from around the globe engaged in debates about the best ways to leverage technology for greater individual freedom.
The three fundamental papers of the Cypherpunks

The cypherpunk movement, deeply rooted in digital activism and cryptography, drew upon several foundational texts to articulate its principles and vision for the future. Among these writings, three stand out in particular:
"A Cypherpunk's Manifesto": written by Eric Hughes in 1993, asserts that privacy is a fundamental right. The author argues that the ability to communicate freely and confidentially is essential for a free society. The manifesto states: "We cannot expect governments, corporations, or other large, faceless organizations to grant us privacy [...]. We must defend our own privacy if we expect to have any".
"The Crypto Anarchist Manifesto": written by Timothy C. May in 1992, this document explains how the use of cryptography could lead to an era of cryptographic anarchy where governments would be powerless to interfere in the private affairs of citizens. May envisioned a future where people anonymously exchange information and money without the intervention of a third party.
"A Declaration of the Independence of Cyberspace": although not exclusively cypherpunk, this text reflects the sentiments of many participants in the movement. Written in 1996 by John Perry Barlow, it is a response to the increasing regulation of the Internet by governments. The declaration asserts that cyberspace is a distinct realm from the physical sphere and should not be subject to the same laws. As it states, "We have no elected government, nor are we likely to have one".
The predecessors of Bitcoin
Before the emergence of Bitcoin, there had been several attempts to create a digital currency. For example, David Chaum introduced the concept of "anonymous electronic money" with his project "DigiCash" in the 1980s. Unfortunately, due to various constraints, DigiCash never boomed.
Another important precursor is Wei Dai's "B-money". Although it was never implemented, it presented the idea of an anonymous digital currency where fraud detection was performed by a community of evaluators rather than a central authority.
The image below clearly illustrates the development of the movement through its many technological innovations.
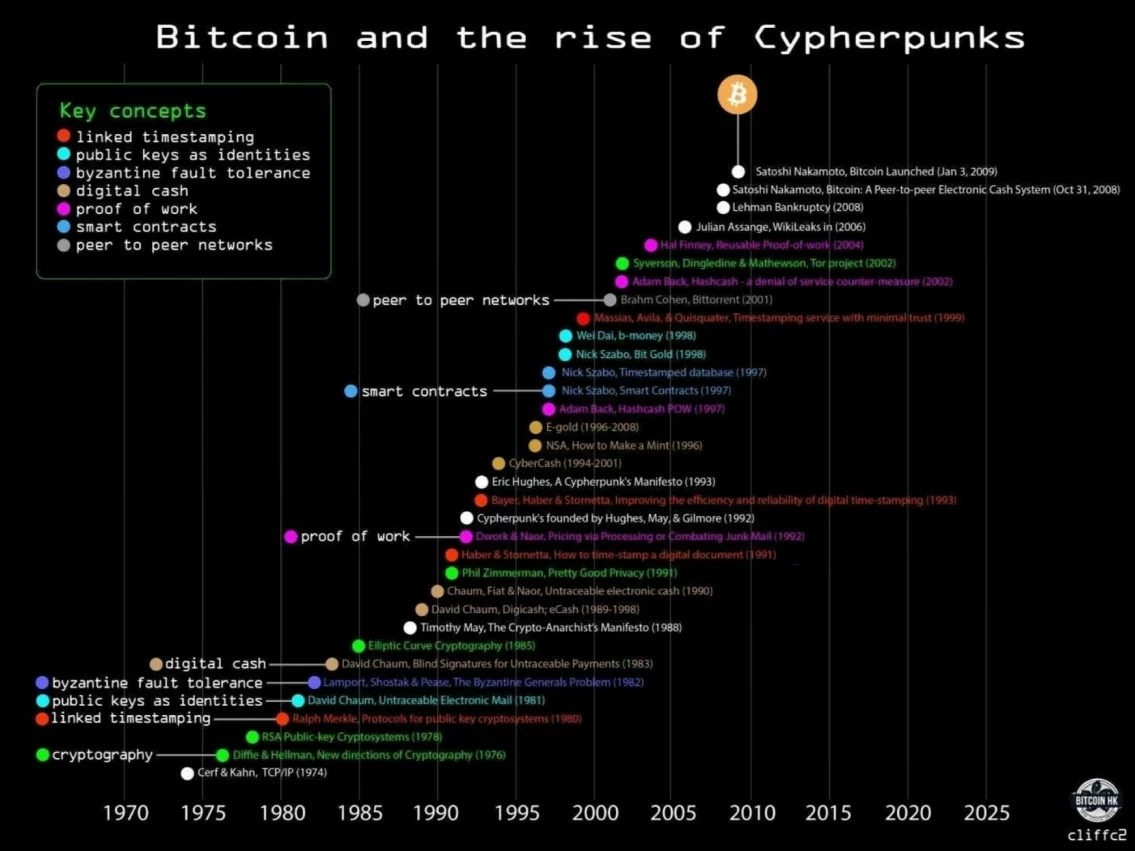
It was in this fertile environment that the mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto published the Bitcoin whitepaper in 2008. In this document, he combined several ideas from the cypherpunk movement, such as proof of work and cryptographic timestamps, to create a decentralized and censorship-resistant digital currency.
However, Bitcoin was more than just that: it represented the achievement of the cypherpunk ideals. Beyond its technology, it symbolized a revolution against traditional financial systems and offered an alternative based on transparency, decentralization, and individual sovereignty.
Conclusion
The prehistory of Bitcoin is deeply rooted in the cypherpunk movement and the collective quest for greater freedom in the digital age. By combining the principles of cryptography, decentralization, and integrity, Bitcoin has become much more than a currency. In fact, it is the product of a philosophical and technological revolution that continues to reshape our world.
Therefore, Bitcoin is a protocol that stretches over long periods of time, and encourages us to question our relationship with energy, time, and money.
However, is Bitcoin a "real" currency? To understand this, we first need to understand the concept of money and its various forms, which we will explore in the next chapter.
If you want to explore Bitcoin's history in more details, we highly recommend our HIS 201 course, where you will discover the origins and the slow emergence of Bitcoin, as well as the beginnings of its history and community. This course is fully documented and sourced, with, of course, many anecdotes:
https://planb.network/courses/a51c7ceb-e079-4ac3-bf69-6700b985a082
Money
Money Throughout History
The evolution of money is a fascinating aspect of human history that reflects the ingenuity of civilizations throughout the ages in meeting constantly evolving economic needs.
From shells to bank accounts
Originally, currency was a tangible asset, such as grain, livestock, or another commodity. However, these goods had the major disadvantage of being perishable, making it difficult to use them as a long-term savings medium. For example, poor harvests or animal illness could destroy an individual's wealth overnight. Thus, as civilizations advanced and trade expanded to new regions, the need for a universal medium of exchange arised. Individuals first experimented with objects such as shells and gemstones, but they were not as durable or scarce as they believed. Eventually, gold became the standard, due to its rarity, durability, and divisibility. It was, and remains to this day, a symbol of wealth and power.

What is the role of money?
Money is a highly sophisticated communication tool:
It allows for communication between the present and the future, because it transforms our time and energy into an asset that can be reused in the time to come without the risk of devaluation.
It facilitates communication in a universal language: without knowing each other or speaking the same tongue, two strangers can exchange, trade, and agree on the value of things.
Its function in our world is difficult to artificially replicate. In fact, no individual or group can create money, as it is a natural phenomenon that must emerge from the market and voluntary consensus. In this sense, prices serve as signals and pieces of information that guide society in allocating resources.
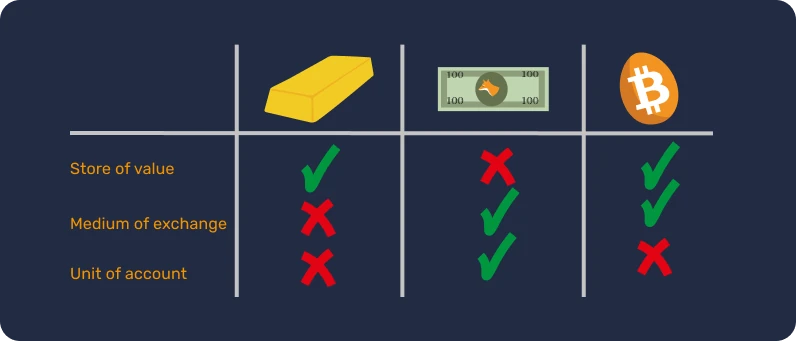
For these reasons, gold as money is the result of 4,000 years of monetary Darwinism based on the following Aristotelian functions:
- Store of value: money can be used to transfer purchasing power into the future, so it needs to be a durable material;
- Medium of exchange: money can be used in exchange for goods and services instead of bartering, thus avoiding the coincidence of wants between traders;
- Unit of account: money also allows us to compare the values of different goods to better understand their relative convenience.



The characteristics of money
Gold ideally meets the criteria of an efficient currency: its natural rarity makes it valuable, while its chemical properties ensure it does not erode over time. These features have made gold a great store of value, but not a common currency, because this form of money is not easily divisible or transportable over long distances. In a globalized and digital world, gold struggles to keep pace and requires a central entity to make it divisible and easily exchangeable (i.e. through minted coins).
On the opposite, state fiduciary currencies (fiat) are easily usable, but are constantly devalued by the entities that control them (kings, central banks, emperors, dictators).
To explain this concept better, we shall explore the characteristics of an effective currency:
- Fungibility, meaning that it is interchangeable with another unit of the same kind without loss of value;
- Divisibility, as it can be divided into smaller units to facilitate transactions of varying volumes;
- Liquidity, which means it is easily convertible into goods or services.
In order to meet these criteria, currency has historically evolved by taking different steps:
- Raw stone -> Coin
- Banknote -> Bank card
- Blockchain -> Lightning Network
Currencies are still evolving to this day, adapting their forms to meet different use cases. As we said, while gold is an excellent store of value, it is no longer suitable for the current globalized economy. Similarly, fiduciary currencies such as the dollar and the euro are very liquid and easily transportable because they are now mostly digital, but their value is constantly lowered by monetary inflation.
On the other hand, Bitcoin presents new possibilities. Its properties, such as the strictly limited supply, make it an excellent store of value. Moreover, as a neutral internet currency, it serves as a viable medium of exchange that transcends borders. However, it is still not widely accepted in commerce today, despite its constant adoption.
Fiduciary currencies
"Those who cannot remember the past are condemned to repeat it" said George Santayana.
A truth that resonates soundly when it comes to the current monetary system.
Fiduciary = Trust
Today, major currencies such as the Euro and the Dollar are considered fiduciary. This means they lack intrinsic value and depend entirely on the trust and confidence we place in the institutions that govern them.
A fiduciary currency is a form of money that is decreed as such by an institution, i.e. a state, like China with the Yuan, or a political-economic union, such as the European Union with the Euro. The entity in charge of its issuance is the central bank (For example, we can mention the People's Bank of China, the Federal Reserve of the United States, or the Central Bank of the Republic of Guinea). It is precisely these entities that are in charge of formulating the monetary policy and therefore how much money should be put into circulation or printed.
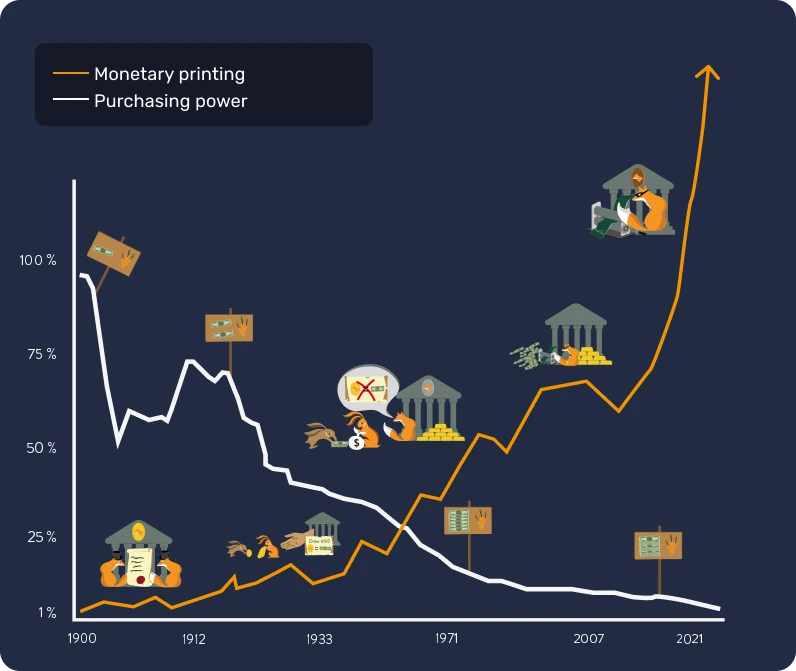
Monetary devaluation: a strategy as old as the Roman Empire
Since antiquity, gold has served as a monetary reference, but its rigidity has often led leaders, whether Roman emperors or modern governments, to adopt alternative currencies, often fiduciary.
The mechanism is simple and is inspired by practices that have existed since the origins of civilization. Leaders, eager to exert control over wealth, begin by centralizing gold, often by exploiting their power and promising protection and security. With this precious reserve in their hands, they introduce a new currency, equivalent in value to gold, but minted in their effigy. This currency then begins to circulate, and people quickly adapt to the convenience of its simple use.
However, these leaders then begin to devalue the new currency in a gradual way, de facto reducing its value by a few percent each year in comparison to the initial gold price. This silent devaluation is often justified as being in the interest of the people. In reality, those who save in this fiduciary currency see the worth of their savings erode, while the state finances its projects through inflation. Furthermore, this devaluation makes debt easier to repay.

At a critical moment, the leader makes the announcement: the currency is no longer backed by gold. The public, now accustomed to the fiduciary currency and often misinformed about financial matters, accepts this reality, allowing the state to freely manipulate the money supply and print enormous sums of money at almost no cost.
Monetary printing then leads to inflation and gradually impoverishes the population. Besides, the financial system is regulated and restricted to avoid its collapse, since any disruption could provoke a major economic crisis. Contrary to the masses, financial institutions and wealthy individuals benefit greatly from this system, which creates an inequality gap and favors authoritarianism. In this context, they are not incentivized to make radical changes, allowing the system to continue its course until a possible implosion.
When well executed, this strategy can last for decades. However, it is important to note that a very fast devaluation or loss of confidence can lead to hyperinflation (see next chapter). History shows that the dollar has lost 98% of its value in 100 years, the euro 30% in 20 years, and the pound sterling 99% since its creation.
In the end, the currency may no longer have any connection to gold, similarly to Roman coins at the end of the Empire, or even be reduced to a simple numerical value, disconnected from tangible reality.
Today, we are witnessing a historic turning point. The dollar, which has long dominated, appears to be in decline, while gold has lost its central role. We stand at the threshold of a new monetary cycle, reminding us that the lessons of history are often forgotten
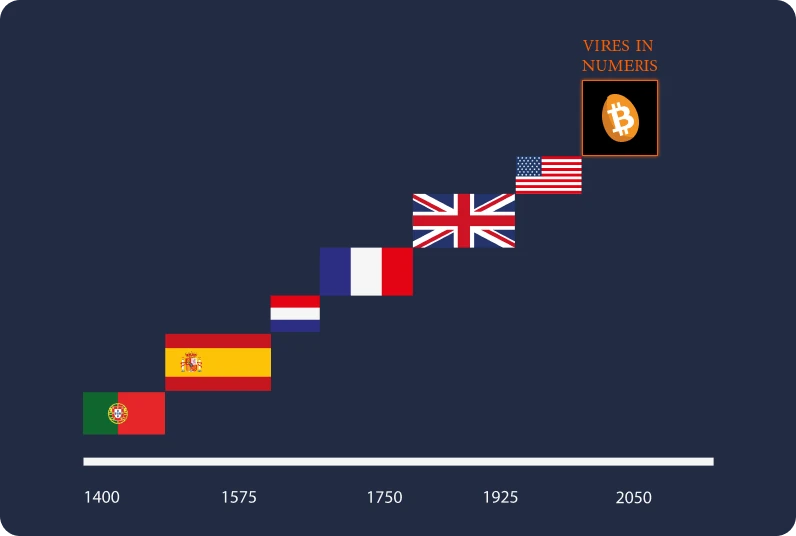
Is Bitcoin a solution?
Because of these premises, the Bitcoin revolution is gaining momentum. Contrary to previous currencies, it requires no trusted third party and aims to separate the State from money.

In fact, Bitcoin presents itself as a response to these systemic challenges by proposing a decentralized solution and a new parallel monetary system. Historically, if gold has been favored as a currency due to its resistance to counterfeiting, Bitcoin similarly cannot be falsified. Moreover, it is limited to 21 million units, thanks to its decentralized and cryptographic nature. Bitcoin is a currency that relies on transparency and neutrality, offering an attractive alternative to the current centralized monetary system.

Another reason why Bitcoin has acquired attention is the emergence of central bank digital currencies, or CBDCs, which seems inevitable. This new form of money would develop a more centrally planned economy, and could both hinder individuals' financial freedom and facilitate authoritarian abuses. We can conclude this chapter with the quote from the Nobel Prize winner F.A Hayek in 1984:
"I don't believe that we should ever have a good money again, before we take the thing out of the hands of the government. If we can't take them violently out of the hands of the government, all we can do is by some sly or roundabout way introduce something they can't stop."
To learn more about economic fallacies and freedom, we invite you to discover our ECO 102 course, which traces the life and ideas of Frédéric Bastiat, a 19th-century French thinker who would surely have appreciated the emergence of Bitcoin:
https://planb.network/courses/d07b092b-fa9a-4dd7-bf94-0453e479c7df
Hyperinflation
Hyperinflation is a monetary phenomenon that is specific to fiat currencies: it is charterized by a complete loss of confidence in a currency and a drastic increase in inflation due to monetary printing by authorities. As a result, the savings accumulated by individuals can dissipate in a relatively short period of time, pushing the country on the brink of economic, social, and political collapse.
Inflation running wild!
In order to understand the impact of inflation on savings, we need to take different inflation rates into consideration.
- With a 2% inflation, you lose 2% of your purchasing power annually, which amounts to 10% over 5 years.
- With 7%, you lose half of it in 10 years.
- With 20%, you lose almost half of it in 3 years.
When hyperinflation occurs, we are no longer talking about 20% per year, but rather 20% per month or, at its peak, even per DAY. Experiencing a 100% inflation per day over three days is a realistic scenario that has occurred and continues to happen in our world.
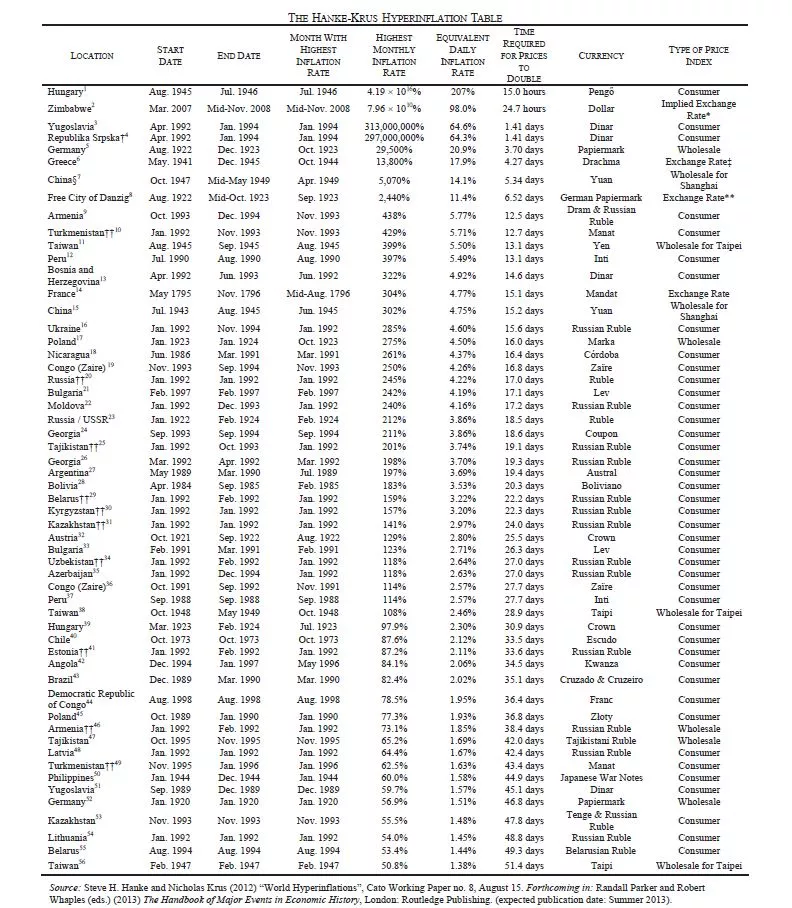
It is crucial to understand that hyperinflation does not happen by chance, by capitalism, or by political attacks from opponents. Hyperinflation is the direct consequence of bad monetary decisions made by central bankers and politicians. Its aftermaths affect every citizen and even impacts next generations. We kindly invite you to spend five minutes reading the following table to fully realize the real impact of this phenomenon (the ECO204 course further delves into this subject). As you can see, no country or currency is potentially safe.
What are the phases of hyperinflation?

For hyperinflation to occur, certain events must take place.
Phase 1 - Loss of confidence
- Centralization of monetary power facilitates the creation of money and its abuses. In this context, external factors like wars, government policies, or rising prices of key resources — such as wheat or gasoline — can trigger hyperinflation. Thus, a loss of confidence in a currency can arise, and individuals begin to question the origin of money and the benefits of mandated monetary policy.
Phase 2 - Currency collapse and price increase
- As governments lose control of trust, individuals begin to exchange their currency for a more stable one, like what happened in Venezuela with the US dollar. This circumstance leads to a rise in prices, creating a vicious circle where goods and services become increasingly expensive. To meet these needs and correct the monetary policy, the state prints more money, resulting in exponential inflation.
Phase 3 - The vicious circle of money printing
- Thus, more and more bills are needed to purchase goods, which results in the scarcity of paper money. In response, governments resort to printing more bills, which fuels inflation even further.
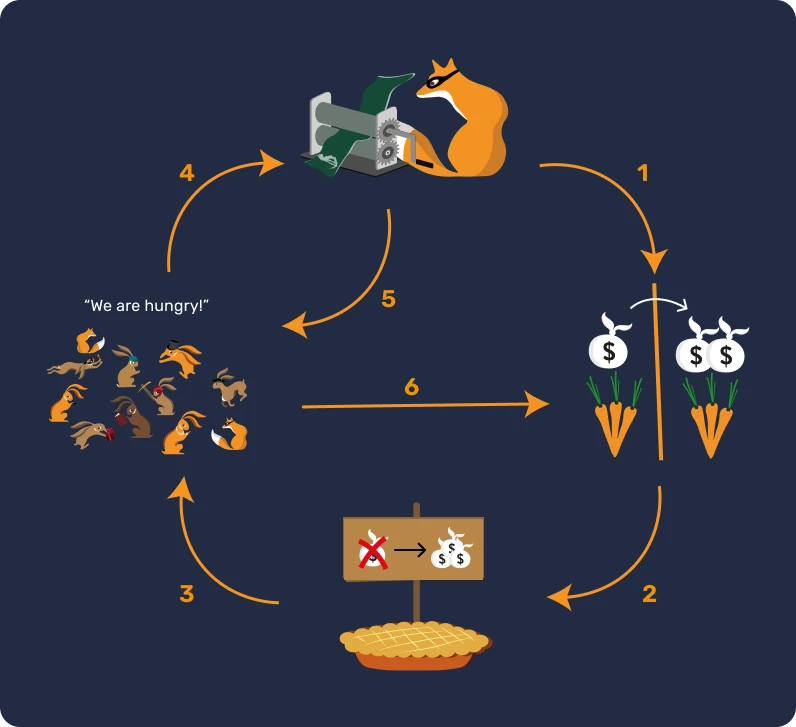
Phase 4 - The emergence of a new currency
- A new currency is then introduced to replace the old one, in order to break the cycle of inflation by implementing stricter controls that were not in place with the previous legal tender.
Resolving a hyperinflation crisis often requires radical changes, such as revolutions, government shifts, central bankers changes, among others. Loss of confidence, currency collapse, and reconstruction are essential phases to revive an economy based on fiat currency.
Three notable examples
Germany, 1922-1923.
One of the most striking examples of hyperinflation occurred in the German Weimar Republic after World War I.
Germany had borrowed enormous amounts of money to finance war. However, not only did Germany lose the war, but it had to pay billions of dollars in reparations. The month with the highest inflation rate was October 1923, peaking at 29,500%, which was equal to an inflation rate of 20.9% per day. Prices doubled every 3.7 days! The German currency became so useless that some citizens preferred to burn their paper money instead of wood because it was actually cheaper. It is even told that in restaurants, waiters had to announce the menu prices every 30 minutes to account for inflation.
In the end, the authorities created a new currency, backed by the debts of Germany, France, and England, and guaranteed by German land.

Hungary, 1945-1946
The country that experienced the worst period of hyperinflation to date is by far Hungary after World War II.
Hungary found itself on the losing side of the conflict, with most of its industrial production capacity destroyed. The month with the highest inflation was July 1946, which saw a staggering price inflation of 41,900,000,000,000,000%, equivalent to 207% per day. Prices doubled every 15 hours!
The last banknote to be put into circulation was a 100 million billion Pengo (100,000,000,000,000,000) in 1946.

Zimbabwe, 2007-2008
Until the year 2000, Zimbabwe was self-sufficient for almost all of its needs except for oil.
In 1997, the Zimbabwean dollar collapsed by over 72% after the government agreed to compensate war veterans for the equivalent amount of 450 million US dollars. Since the government did not have such an amount in its supplies, it resorted to running the printing press. In 2005, inflation reached 586%, but the peak was in mid-November 2008 with a rate estimated at 79,600,000,000% per month.
In June 2007 the government had already reacted by imposing price controls, but this action did not have any influence on the economy. Stores were actually looted, and merchants no longer had the means to restock their shops.
In April 2009, the Minister of Finance announced the suspension of the Zimbabwean dollar and authorized the use of different foreign currencies for trade. All bank accounts, pensions, and financial institutions saw their balances evaporate overnight.

In conclusion, hyperinflation has the effect of rapidly degrading the value of the currency, leading to the erosion of savings and the loss of confidence in the monetary system. As Voltaire once suggested, a fiat currency will always eventually lose its intrinsic value and converge towards zero. A currency that relies on a trusted third party like a financial institution is, in practice and in the long term, a defective one, because it is unable to guarantee purchasing power or preserve savings.
To delve deeper into the subject of hyperinflation, we recommend David St-Onge's ECO 204 course, where you will learn what hyperinflationary cycles are and their real impacts on our lives. You will also discover the similarities between these cycles and, most importantly, how to protect yourself from them.
https://planb.network/courses/caa75343-ac90-4249-bcca-0e2e57c3a0f1
21 million bitcoins
Bitcoin's monetary policy
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency with a pre-defined maximum quantity of 21 million units. This intrinsic characteristic of scarcity is determined by its computer code and reinforced by the consensus of all users participating in the protocol.
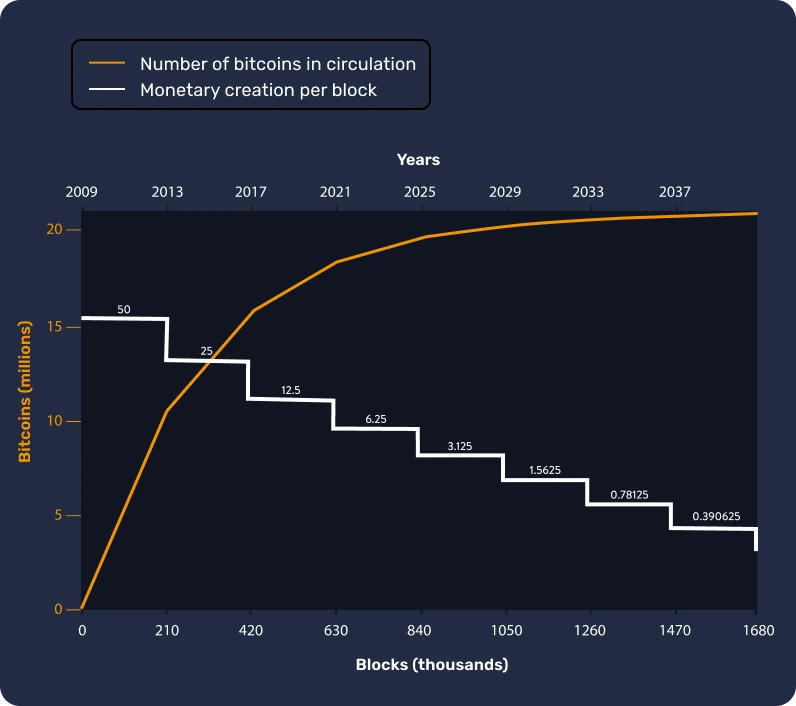
Its monetary issuance can be illustrated by a curve that represents the quantity of bitcoins created over time. For example, in 2022, approximately 18.5 million bitcoins were in circulation. Forecasts indicate that by 2025, there will be around 19.5 million bitcoins, representing around the 93% of the total supply, and by 2037, this figure will reach 20.4 million.
How are new bitcoins created?
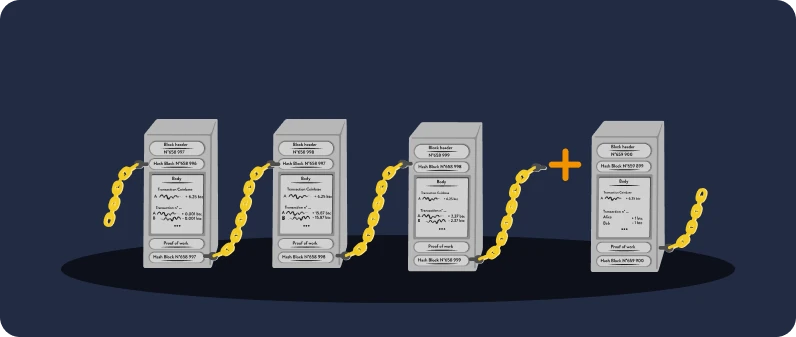
The creation of new bitcoins is the result of the mining process. In a nutshell, miners use powerful computers that solve complex mathematical problems (hash), which validate and secure transactions. Once a problem is solved (or a valid hash is found), the miner adds a new block of transactions to the blockchain, a decentralized and distributed ledger that records all transactions made on the network. The blockchain ensures transparency and security, as each block is linked to the previous one, making it nearly impossible to alter past data without consensus from the network.
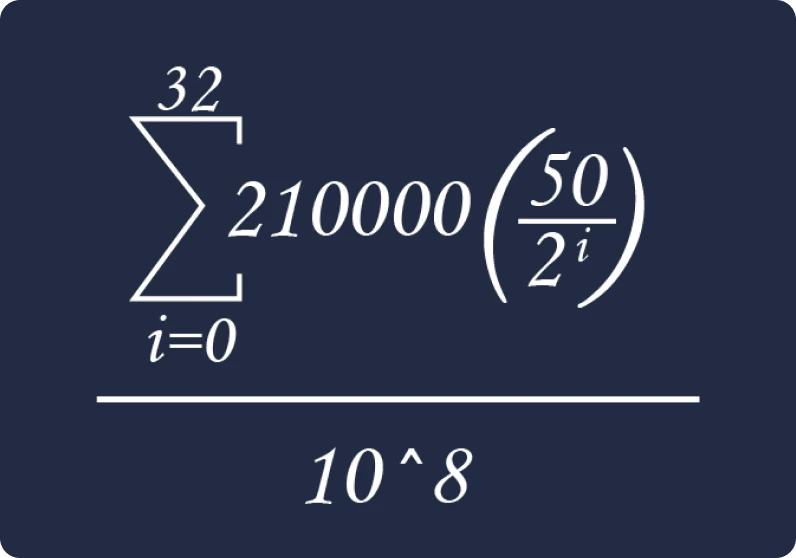
After successfully performing this task, miners get rewarded with the issuance of new bitcoins every ten minutes. This reward is programmed to halve every 210,000 blocks, which is approximately every four years (an event known as "halving"), giving the monetary issuance curve a stair-like shape. Due to this mechanism, it can be mathematically predicted that the creation of new bitcoins will cease arount the year 2140, when the total number reaches its limit of 21 million.
| Halving Number | Block Height | BTC Reward After Halving | Estimated BTC in Circulation After Halving |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 210,000 | 25 BTC | 10,500,000 BTC |
| 2 | 420,000 | 12.5 BTC | 15,750,000 BTC |
| 3 | 630,000 | 6.25 BTC | 18,375,000 BTC |
| 4 | 840,000 | 3.125 BTC | 19,687,500 BTC |
| 5 | 1,050,000 | 1.5625 BTC | 20,343,750 BTC |
| 6 | 1,260,000 | 0.78125 BTC | 20,671,875 BTC |
| 7 | 1,470,000 | 0.390625 BTC | 20,835,937.5 BTC |
| 8 | 1,680,000 | 0.1953125 BTC | 20,917,968.75 BTC |
| 9 | 1,890,000 | 0.09765625 BTC | 20,958,984.375 BTC |
| 10 | 2,100,000 | 0.048828125 BTC | 20,979,492.188 BTC |
| 11 | 2,310,000 | 0.0244140625 BTC | 20,989,746.094 BTC |
| 12 | 2,520,000 | 0.01220703125 BTC | 20,994,873.047 BTC |
| 13 | 2,730,000 | 0.006103515625 BTC | 20,997,436.523 BTC |
| 14 | 2,940,000 | 0.0030517578125 BTC | 20,998,718.262 BTC |
| 15 | 3,150,000 | 0.00152587890625 BTC | 20,999,359.131 BTC |
| 16 | 3,360,000 | 0.000762939453125 BTC | 20,999,679.566 BTC |
| 17 | 3,570,000 | 0.0003814697265625 BTC | 20,999,839.783 BTC |
| 18 | 3,780,000 | 0.00019073486328125 BTC | 20,999,919.892 BTC |
| 19 | 3,990,000 | 0.000095367431640625 BTC | 20,999,959.946 BTC |
| 20 | 4,200,000 | 0.0000476837158203125 BTC | 20,999,979.973 BTC |
We will revisit the concept of mining in more details in the miner chapter.
Guaranteeing digital scarcity
The limit of 21 million is the basis of Bitcoin scarcity, and is guaranteed by two key mechanisms: the adjustment of mining difficulty and the game theory.
- The mining difficulty adjustment is a process that takes place every 2016 blocks, or around two weeks, to ensure that a new block is added to the blockchain every ten minutes on average. This frequency of block creation and the total quantity of bitcoins are both fixed aspects of the Bitcoin protocol and cannot be changed without a general consensus, unlike the arbitrary decisions made in traditional monetary systems.
The difficulty of finding a valid hash follows a sort of cycle: if the number of miners increases and more blocks are found faster, this causes a decrease in the average time to find a block and so the difficulty is increased. As a consequence, the number of blocks that miners find is lowered, which means that the mechanism goes back to the average of 10 minutes per block. Please see the image below for a visual display.
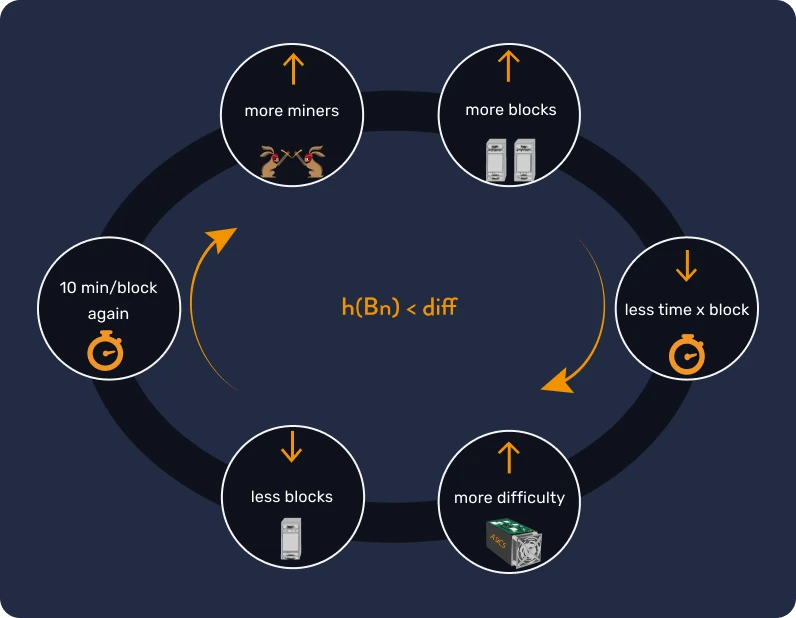
Conversely, if fewer miners work and blocks take longer, the mining difficulty decreases, speeding the average block time back up.
Did you know that miners are incentivized to mine a block in order to earn new bitcoins through the block subsidy, as well as transaction fees from the transactions they include in that block?
Thus, as the number of bitcoins issued approaches the 21 million limit, miners will be remunerated more through their transaction fees than through the block subsidy.
- Game theory is a mathematical concept that relies on human rationality. It assumes that individuals act logically, seeking to maximize their own benefits while considering the potential decisions of others. In Bitcoin, game theory helps to ensure that the majority of miners and users will act in the best interest of the network. In fact, since protocol changes are voted by the users, any modification to the Bitcoin protocol would require the agreement of the entire community of users, which is highly complex. So, if someone wanted to create a 22nd million bitcoin, they would have to convince all users to voluntarily devalue their own savings, which is unlikely to happen because Bitcoin is global and is not governed by a central group.

The idea of devaluing the currency goes against the fundamental philosophy of Bitcoin, so a change in its overall quantity is highly unlikely to happen.
An auditable monetary policy: every second, from the beginning and forever!
The scarcity of Bitcoin is a major asset, and the maximum quantity of 21 million bitcoins in circulation is public and verifiable by anyone.
In fact, anyone can do this through a Bitcoin node (i.e. a transaction
validator) by simply entering the following command: bitcoin-cli gettxoutsetinfo. This transparency strengthens trust in the Bitcoin system, which is not
based on central institutions or individuals, but rather on the mathematical
and cryptographic guarantees inherent in its protocol (You will learn how to
do this easily in LNP201).
{
"height": 710560,
"bestblock": "0000000000000000000887384d67103412ea7f18a43953e65c8c4ac36bf42e54",
"transactions": 473244,
"txouts": 1018917,
"bogosize": 2183872374,
"hash_serialized_2": "eebb9987337700ffaacbbaa11223344",
"disk_size": 178239584,
"total_amount": 18745998.12345678
}
Bitcoin guarantees a sound monetary management by limiting its creation by design, which makes it very different from other currencies because it can protect users' savings. Aligned with the principles of Austrian economics, its stable quantity and predictable distribution protect it from the inherent risks of inflation that traditional currencies have to face (see the ECO201 course to know more).
In summary, Bitcoin, with its decentralized nature, programmed scarcity, and transparency, offers a unique alternative to traditional monetary systems. It illustrates how technology can be used to create a currency that not only is useful and verifiable, but also preserves the value of users' savings by strictly limiting its supply.
Conclusion of section 2!
Bitcoin Wallets
What are Bitcoin wallets?
In section 2, we are going to explore the storage and security of Bitcoin through the use of wallets, in order to understand where these famous bitcoins are located and how to interact with them!
Demystifying Bitcoin wallets
We use wallets to interact with the Bitcoin network in three main ways:
- To receive bitcoins
- To send bitcoins
- To secure them against hacking and theft attempts
A Bitcoin wallet can have many shapes and forms: a software on your computer, an application on your smartphone, a physical device like a USB key, or even a piece of paper. Each of them serves different use cases. In fact, some are designed for large transactions with an emphasis on security, while others prioritize privacy, or they are intended for daily payments of small amounts.
Portfolios can thus be categorized into broad families of use, always centered around a key question: are you the owner of the funds or are you leaving control of your money to a third party? We will explore this topic in detail in the next chapter, but the question remains straightforward: is the money in your pocket or in your banker's pocket?

How does a Bitcoin wallet work?
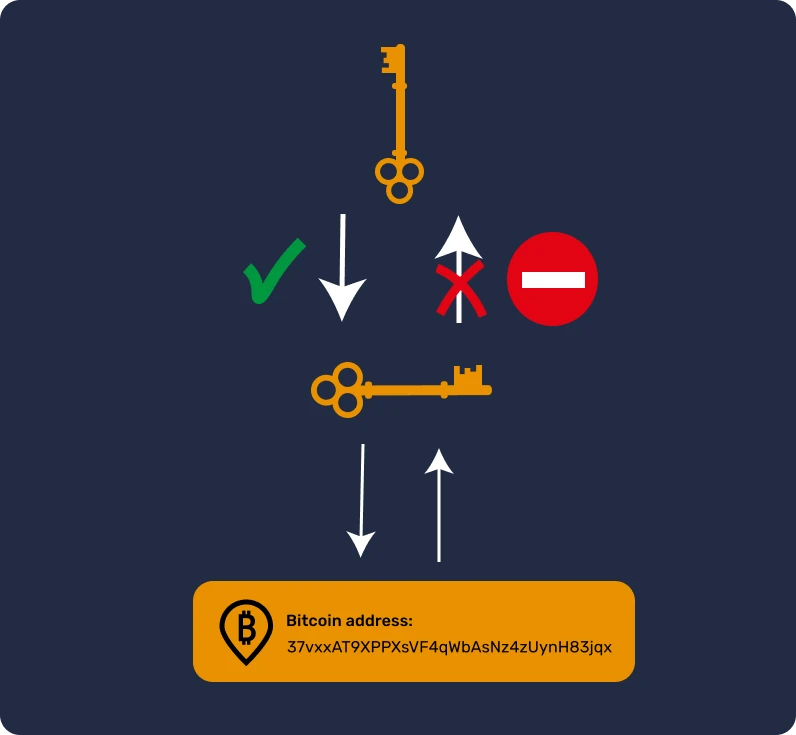
Whether it's your Bitcoin "banker" or yourself, the vast majority of Bitcoin wallets work with a similar technology based on asymmetric cryptography, which involves a system of key pairs: a private key for spending and a public key for receiving.
Private key
When initializing a wallet, a secret recovery phrase, also known as a mnemonic phrase (private key), is generated and presented to you in the form of 12 or 24 words.
The private key is fundamental because it constitutes the ownership of the bitcoins and therefore the right to use or send them. Therefore, the holder of the private key is the true owner of the bitcoins. As the popularized statement goes, “Not your keys, not your coins.”
This key must be kept secret and well protected, as it unlocks your fortune!
Public key & address
The public key is generated from the private key and it is linked to it. Sharing the public key poses risks to privacy (because other users can see your balance) but not to security (because they cannot spend your funds without possessing the private key). In turn, the public key is used to create Bitcoin addresses, and thus receive money.
These addresses are automatically created by your wallet and can be shared securely. To maximize your privacy, it is advisable to use them only once.
In a summary, this technology empowers us to receive bitcoins without enabling the receiver to steal our funds! A mailbox could be a fitting metaphor: people can deposit money into it, but you are the only one who can open it.
Are bitcoins in the wallet?
Although your keys are stored in your wallet, the bitcoins themselves are actually "stored" in the Bitcoin blockchain, which is a public distributed ledger within the Bitcoin peer-to-peer network (we will delve into it in section 3). This means that losing the device containing your wallet does not necessarily result in the loss of your bitcoins. What allows you to recreate your wallet and spend your bitcoin is actually the private key, so always remember to secure it properly!

Fortunately, since 2017, the private key can be represented by a simple list of 12 or 24 words, known as 'mnemonic phrase, which are quite easy to save. This phrase serves as a backup for your funds and allows you to recreate your wallet using any Bitcoin wallet software or app. Therefore, anyone who finds this list of words can access your bitcoins.
What about hackers?
What if someone accidentally guesses our list of 12 or 24 words? The short answer is that it is highly unlikely, thanks to the cryptography used to create the wallet. To put it into perspective, accidentally discovering your same mnemonic phrase is akin to finding the "right" number between 1 and 2 raised to the power of 256, which is almost equivalent to finding the "right" atom in the Universe. However, if you are not satisfied with this default security, you can always enhance it by adding a passphrase (an extra word) to your Bitcoin wallet.

Thus, the probability of hacking your Bitcoin wallet is astronomically low if you follow the good security practices that we will detail in the next section.
Keep in mind to choose the right wallet for your needs and usage: detailed tutorials on managing and securing different wallets are available in the tutorial section of our university.
If, during your journey down the rabbit hole, you want to learn more about building a Bitcoin wallet, from entropy to receiving addresses, we recommend the CYP 201 course dedicated to this topic:
https://planb.network/courses/46b0ced2-9028-4a61-8fbc-3b005ee8d70f
Bitcoin Wallets and Security
Asking the right questions before starting
When you own bitcoins, the security of your funds is a major concern. The best way to define a security level that is suitable for your situation is to ask yourself a series of questions:
- Who can access your funds? In other words, do you have sole access to your bitcoins, or does a third party (such as a company) grant you access to your funds?
- How do you plan to use the bitcoins in that particular wallet? Regularly? For medium-term, or long-term savings?
- What are your technical skills?
- What is your security budget?
There is actually no universal answer or solution, so take the time to answer these questions, as it will help tailor your security measures to your needs.
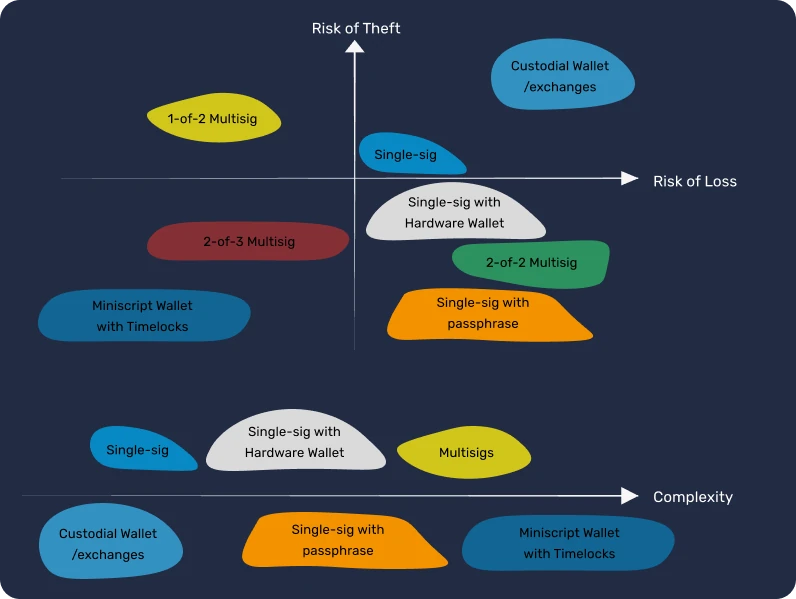
Thinking about Bitcoin wallets in terms of complexity
Here below, we will define several levels of security:
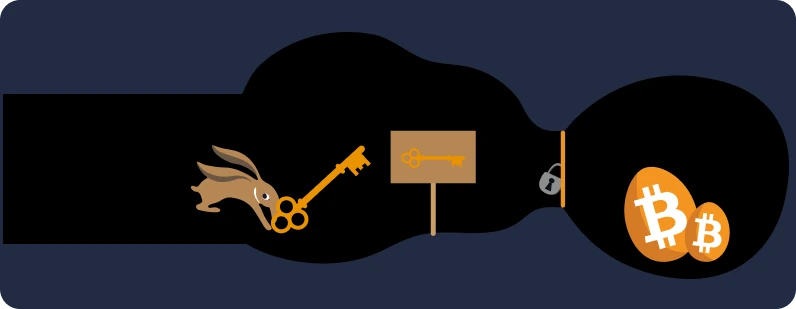
- Level 0, you use a so-called "custodial service" where you are not the sole holder of your bitcoins. Be aware that this trusted third party can restrict your access to your funds at any time. In this case, your level of financial sovereignty is similar to that of a traditional banking system with a bank account.

- Level 1, you use a Bitcoin wallet on your phone or computer, where you are the sole holder of your bitcoins and you can easily carry out your transactions. The afore-mentioned tool is referred to as "hot wallet", because the private key is stored on a device with internet access. In this case, it is crucial to back up your mnemonic phrase to regain access to your funds in the event of losing your phone or computer.
For example, you can use Sparrow Wallet as a hot wallet:
https://planb.network/tutorials/wallet/desktop/sparrow-c674e2ac-d46f-4c82-92a7-7d1b0e262f5d
- Level 2, you use a physical wallet, and you have secured your list of 12/24 words. It is often referred to as "cold wallet" because your keys are stored on a device that is not connected to the internet. In this case, you will always need to sign every transaction with your device, which makes your funds less accessible on a daily basis.
For example, you could use a Ledger, a Satochip, or a Tapsigner:
https://planb.network/tutorials/wallet/hardware/satochip-e9bc81d9-d59b-420d-9672-3360212237ba
https://planb.network/tutorials/wallet/hardware/tapsigner-ab2bcdf9-9509-4908-9a4a-2f2be1e7d5d2
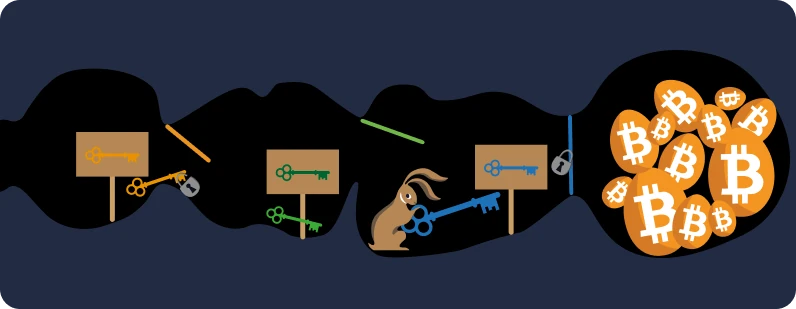
- Level 3, you use a level 1 or 2 wallet, but you added an additional passphrase. In this case, be aware that you need to backup both the list of 12/24 words and your passphrase. Ideally, these two pieces of information are stored in two different places.
To learn more about the use and functioning of the BIP39 passphrase:
https://planb.network/tutorials/wallet/backup/passphrase-a26a0220-806c-44b4-af14-bafdeb1adce7

- Level 4, you use a set of wallets to create a "multisig" wallet, which means that multiple signatures are required to conduct a transaction. In this case, be aware that each part of the multisig should be stored in different locations. This approach is often considered an advanced use of Bitcoin, primarily for managing large amounts and for corporate purposes.
Of course, different use cases also require different Bitcoin wallets, and there is no one-size-fits-all solution.
Security must be adapted
The amount one is willing to leave on a specific security level depends on each individual. For some, leaving 1 BTC on a hot wallet is reasonable, while, for others, it is the opposite. In any case, when you want to secure a small amount, we advise not to spend too much on security by buying a physical wallet. Besides, keep in mind that overcomplicating the security and accessibility of your bitcoins can be detrimental, especially if you mishandle the backups of your wallets.
In conclusion, direct ownership of one's bitcoins is an essential element to ensure financial sovereignty. It is recommended to use a mobile wallet for daily expenses and an offline, or "cold," physical wallet to store larger amounts. Businesses, on the other hand, should consider using multi-signature systems, or "multisig," for increased and shared security. It is also essential to avoid custodial services, which can replicate some vulnerabilities of the traditional financial system.
With this in mind, we can now move to the next section where we describe how to create a Bitcoin wallet. However, if you wish to further explore the topic of security, you can read this article by DarthCoin.
Setting up a Wallet
The security of your bitcoins has crucial importance, and a simple mistake can have disastrous consequences. That is why we need to learn the best practices to adopt when creating a new Bitcoin wallet.
Please note that the BTC102 course will guide you through this step.
https://planb.network/courses/f3e3843d-1a1d-450c-96d6-d7232158b81f
This step is no joke!
When you set up a wallet, the software usually creates your private key, usually represented by a list of 12/24 words (often called "seed phrase" or "mnemonic phrase"): these words constitute the access to your funds. If this key is ever revealed to a third party, you should consider the associated funds to be compromised. Therefore, when setting up your wallet, it is essential to follow these rules:
- Cover all cameras.
- Do not take a photo of the word list.
- Do not enter it on a computer or phone.
- Do not save it as a contact or send it to yourself via SMS.
- Never leave your words unattended on your desk.
- Never hide your word list in an unusual place.
You should literally take a blank sheet of paper or print this template, and write the word list with a pen, following the presented order neatly and clearly. Be aware that if the ink fades over time, you may lose your funds. Therefore, it is important to keep this piece of paper protected from those environmental factors that could potentially damage it, like moisture or fire.
Please find an example of how to compile the paper here below: the words are fake, so do not use them!

Our tips for doing it right
Be sure not to make any mistakes while clearly and legibly copying the mnemonic phrase, otherwise your heirs may struggle to read it and could be unable to recover the funds. Once you have saved the words, it’s advisable to create a second copy and store it in a different location from the first. This ensures you have a backup in case the original is lost or damaged.

The word lists should be stored in a safe place that you can easily remember. Avoid creating overly-complicated hiding plans that could lead to losing them.
Your words = your money.
Both 'cold' and 'hot' wallets use the word list method as the standard for backing up private keys. As a result, you can enter your mnemonic phrase into any compatible wallet software or device to restore your access. On the other hand, we strongly advise against using wallets that do not provide a seed phrase, as they may require you to provide an account, an email address, or, even worse, an ID.
ATTENTION: The absence of a list of 12/24 words should alert you.
If you wish to discover, step by step, how to set up your own wallet and get your first bitcoins, we recommend taking this other course:
https://planb.network/courses/f3e3843d-1a1d-450c-96d6-d7232158b81f
Passing the Test of Time
Like any form of wealth, your bitcoins must be protected against loss, theft, and degradation, especially over the long term. Safeguarding your bitcoins requires some technical knowledge and an understanding of the associated risks, which opens the way to two main strategies: engraving your bitcoins on a steel plate and establishing an inheritance plan.
Engraving in steel
One method to secure your bitcoins in the long term is to engrave your mnemonic phrase on an extremely durable material like steel. Doing this creates a physical backup of your keys that is resistant to both water and fire damage.
Various solutions are available: some of them are low-cost, such as the "Blockmit", while others may require more specialized equipment. You can explore this topic further in the tutorials section of our academy.
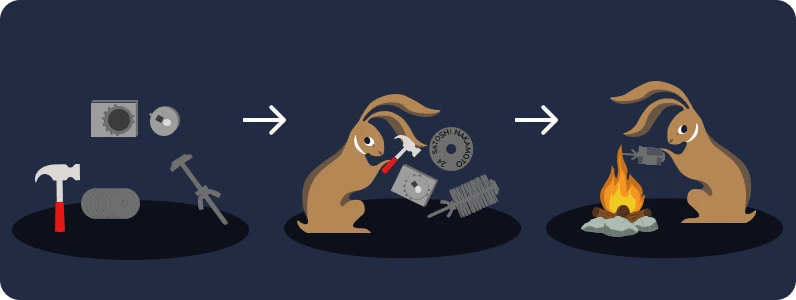
Think about the next generation!
Alongside this first practice, creating an inheritance plan is a crucial step to ensure that your bitcoins are properly managed after your death. This plan involves handwriting a letter where you outline the nature of your assets, their access methods, and the contact information of the trusted individuals who have responsibility over them. It’s also important to discuss the inheritance of bitcoins with an accountant and/or estate attorney to ensure tax compliance, even if this person should never be entrusted directly with the management of your bitcoins.
If you wish to further explore the subject of the inheritance plan for your bitcoins, we recommend reading Pamela Morgan's book Cryptoasset Inheritance Plan or enrolling in the BTC102 course, where we provide guidance on creating your plan.

Privacy is important
In addition to creating physical backups and developing an inheritance plan, privacy is another important topic when it comes to the long-term security of your bitcoins. For example, it is preferable to buy bitcoins without providing identification to minimize the risks of identity theft or tracking of your funds by those entities with the right tools.
Regarding privacy, it is crucial to avoid talking to anyone about your bitcoins. We cannot predict how this technology will be perceived in the future, so maintaining discretion about your ownership is a wise choice: you don’t want to draw attention to yourself or your wallet.
Similarly, avoid openly sharing details about your security system during bitcoin meetings or encounters with strangers...
Summary on Bitcoin Wallet Security
Bitcoin wallets allow you to access bitcoins and make transactions. There are several types:
- mobile or PC wallets, convenient for small amounts and/or regular expenses;
- physical wallets, more suitable for storing bitcoins in the medium and long term;
- multisig wallets, which are more complex to manage and require multiple signatures to perform transactions.
When creating a wallet, it is extremely important that you first backup your list of 12 or 24 words on a piece of paper or a metal plate. This so-called mnemonic phrase allows you to restore your wallet through any Bitcoin wallet application. Be aware that anyone who gains access to this list also gains access to your funds.
In the world of Bitcoin, financial sovereignty is closely tied to individual responsibility, making it essential to secure access to your wallets and backups. To achieve this, it’s important to follow certain guidelines:
- Create an inheritance plan to ensure that your loved ones can retrieve the money in case of any problem.
- Avoid leaving your Bitcoins on exchange platforms as they can be susceptible to hacker attacks.
- Adapt your level of security to your needs and use cases, in order to choose well among the many different Bitcoin wallets available.
Now that we have covered the basics of Bitcoin wallets and the best practices for securing them, in the next chapter we will explore the technical features of Bitcoin. Once again, understanding the basics of the Bitcoin protocol will enhance your comprehension of how it works, empowering you to make better use of it.
The Technical Aspects of Bitcoin.
Launching Bitcoin
Let's start with a bit of history.
October 31, 2008 marks the birth of the new financial technology that is Bitcoin. On this day, the anonymous Satoshi Nakamoto presented his innovation to the world through an email sent to the mailing list of the cypherpunks, a community of cryptography enthusiasts dedicated to promoting privacy on the internet. This email contained a document called "White Paper", which presented how Bitcoin worked.
This initiative did not immediately generate enthusiasm, probably because of the previous failures in the attempts to create a digital cash systems. Nevertheless, this White Paper eventually became a reference for Bitcoin users and has been the subject of many debates in the Bitcoin ecosystem through the years.

On January 3, 2009, Satoshi officially inaugurated the Bitcoin network by creating the first block, also known as the "Genesis block", which marked the launch of the Bitcoin blockchain. This block contains a revealing message reflecting the mission of Bitcoin: "03/jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks."

"We can win a major battle in the arms race and gain a new territory of freedom for several years.” - Satoshi Nakamoto
The Bitcoin protocol comes to life
On January 9, 2009, Satoshi announced the release of Bitcoin 0.1.0 version. Shortly after, Hal Finney took hold of the software and joined the network, which marked the presence of two nodes and, therefore, two miners in the network. Finney even immortalized this step by tweeting, 'Running Bitcoin'. On January 12, 2009, the first Bitcoin transaction of 10 BTC was made between Satoshi and Hal Finney, and you can easily find it, if you go back to block 170.
Interest in Bitcoin grew rapidly, leading many people to test it, engage in debates, solve bugs, and reflect on its ethical, economic, and philosophical aspects. People were so captivated that Satoshi created the BitcoinTalk forum on November 22, 2009, in order to facilitate these types of communications. The forum quickly became the preferred place of discussion for Bitcoin users, so much so that famous memes and symbols associated with Bitcoin were born from it, such as the Bitcoin logo, the famous Hodl, or even Pizza day.
Did you know? On May 22, 2010, Laszlo Hanyecz made history by offering to buy two pizzas for 10.000 BTC: it was the first time that Bitcoin was used to purchase physical goods.

The disappearance of Satoshi Nakamoto
In 2010, as Bitcoin started attracting media attention, Satoshi decided to distance himself by announcing his departure in a forum post on December 12, 2010. On April 23, 2011, he made his last known private exchange via email, then disappeared, leaving his creation in the hands of the community.
“Governments are good at cutting off the heads of a centrally controlled networks like Napster, but pure P2P networks like Gnutella and Tor seem to be holding their own.” - Satoshi Nakamoto
Despite Satoshi's absence, Bitcoin continued to be developed: the history of Bitcoin is written every 10 minutes, and the protocol continues to function to this day as intended. Regardless of any fear, uncertainty, or doubt, Bitcoin continues to move forward, with a very strong online availability. In fact, according to this website, Bitcoin has been functional and running without massive issues for 99.988% of the time since it was created.
For some, Bitcoin is a defined as fungal entity like a mycelium, while others describe it as a black hole. Love it or hate it, Bitcoin continues to exist, with its constant rhythm of 10 minutes per block, like the heartbeat of a new monetary system.
To learn more about Satoshi Nakamoto's writings, we recommend reading "The Book of Satoshi" by Phil Champagne or the ARTE documentary "Le mystaire Satoshi".

“The root problem with conventional currency is all the trust that’s required to make it work. The central bank must be trusted not to debase the currency, but the history of fiat currencies is full of breaches of that trust. Banks must be trusted to hold our money and transfer it electronically, but they lend it out in waves of credit bubbles with barely a fraction in reserve” - Satoshi Nakamoto
Now that we have some background, let's examine how a Bitcoin transaction works in general.
Bitcoin Transactions
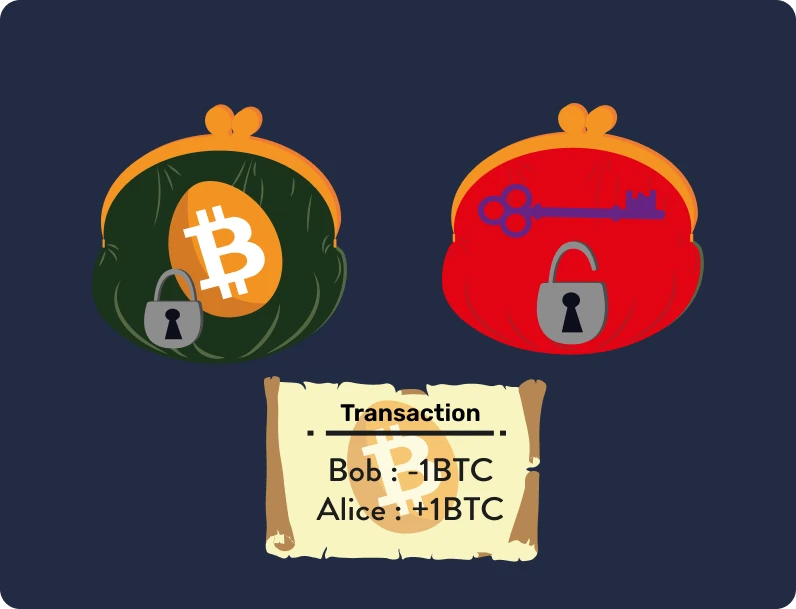
A Bitcoin transaction is simply a transfer of ownership of bitcoins through the use of a Bitcoin address. In order to describe this process, let's introduce two protagonists: Alice and Bob. Alice wishes to acquire bitcoins, while Bob already owns some.
Step 1 - Creating the transaction via the wallet
For Bob to transfer bitcoins to Alice, she must provide him with one of her Bitcoin addresses, which are unique to her Bitcoin wallet. Just like the private key is used to generate the public key, the latter is then used to generate addresses.
In concrete terms, when Alice opens her wallet and presses "receive", a QR code or an address (like this bc1q7957hh3nj47efn8t2r6xdzs2cy3wjcyp8pch6hfkggy7jwrzj93sv4uykr) will be displayed. This serves as her 'Bitcoin IBAN' of sorts, which she then provides to Bob.
Afterwards, Bob makes the transaction by opening his Bitcoin wallet and pressing "send". He then copies and pastes Alice's address into the required field, adds the amount he wishes to send, and decides on the transaction fees, which serve as an incentive for miners to include the transaction in the next block. In fact, the higher the fees Bob pays, the better his chances are of having the transaction included in the next block added to the blockchain, i.e. a public and immutable ledger recording all Bitcoin transactions.
To finalize the transaction, Bob must sign it with his private key to verify that he is the owner of the bitcoins he wants to transfer. This step is usually automatic on mobile wallets, or it takes the form of a confirmation on your physical wallet: "Are you sure you want to send X to Y? Yes or no".

Why do we pay fees? Fees are essential to create a free market for including transactions in blocks. In fact, a block has a size of 1 MB (which was expanded to 4MB after the Segwit update), so the number of transactions that can be "inserted" in a block is limited to a few thousand transactions per block. The size of a transaction depends on its complexity. Therefore, more complex transactions typically incur higher fees.
Step 2: Propagation of the transaction through nodes
At this stage, the transaction has been created and Bob's wallet will share it with the Bitcoin network. To do this, his wallet will communicate with a node of the Bitcoin network, which will propagate this information to other nodes. This kind of process allows the entire network to see this new transaction and take it into account.
At this point, even though this transaction is known to everyone (via a tool called Mempool), it cannot be considered confirmed until it gets inserted in a block by a miner, who is the only one who validates transactions by including them in the blockchain.
In fact, miners have the role of gathering valid and unconfirmed transactions to compile them into a block. In a nutshell, they must solve a cryptographic puzzle in a process called "proof of work" in order for their block to be the next one in the Bitcoin blockchain.
Step 3: The transaction is mined in a block by a miner.
The Proof of work system requires finding a valid "hash" for the block in question: think of it as a unique fingerprint associated with the block, composed of 256 characters. The validity of this hash depends on the difficulty rate of the Bitcoin network (we will go into more details later). For now, consider that a miner has found a valid block, and that Bob's transaction to Alice is included in it. Then, the new valid block is added to the blockchain, the common ledger for all Bitcoin users.
Step 4: The block is valid and verified by Alice's referent node.
At this stage, the transaction is considered valid: the miner will then propagate the new block to the network through their node, and Alice's wallet will be updated.
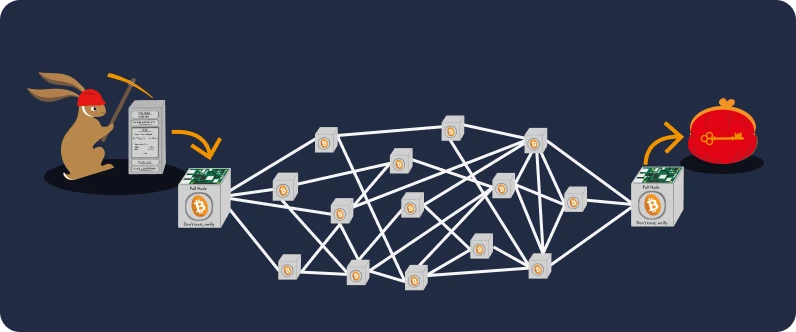
Note: Even if Alice is notified that she has received bitcoins at one of her addresses, it is advisable to consider the transaction immutable only after it has received six confirmations. This means that six additional blocks have to be mined on top of the block containing Bob's transaction. In other words, the older a transaction is in the blockchain, the more immutable it becomes.
What is the importance of this process?
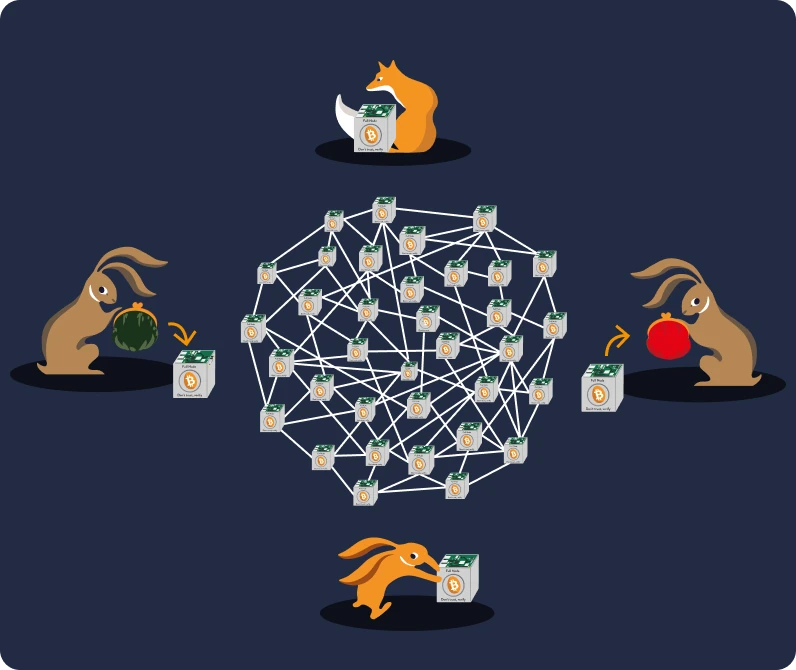
The Bitcoin transaction system is decentralized and works peer-to-peer, without any trusted intermediaries.
Bob sends his transaction to the Bitcoin network, and when a miner publishes a valid block containing Bob's transaction, Alice can start considering that the bitcoins belong to her. Trust is not required at any step of the bitcoin ownership transfer: the protocol rules and economic incentives alone make it prohibitively costly to act maliciously within the Bitcoin system.
In fact, users transfer ownership of their funds by digitally signing transactions with their own private keys. On the other hand, miners hold limited power, and users maintain significant control by using Bitcoin nodes to validate the new blocks and the included transactions. Every node has either a full or a partial copy of the ledger, so the network formed by the Bitcoin nodes makes the system truly decentralized.
As a consequence, for the Bitcoin network to be completely destroyed, every copy of the blockchain on all Bitcoin nodes would need to be eliminated, which is a practically impossible task due to the geographical distribution of these nodes and the difficulty of physically seizing them.
Let's take a closer look at how a Bitcoin node works.
Bitcoin Nodes
Nodes are a fundamental element of the Bitcoin network architecture, as they perform various crucial functions:
- Maintaining a copy of the Bitcoin blockchain
- Validating transactions
- Transmitting information to other nodes
- Enforcing the rules of the Bitcoin protocol.
Therefore, any device running a piece of Bitcoin software, called a Bitcoin node (often using Bitcoin Core), contributes to the decentralization of the network.

Nodes are the central core of Bitcoin.
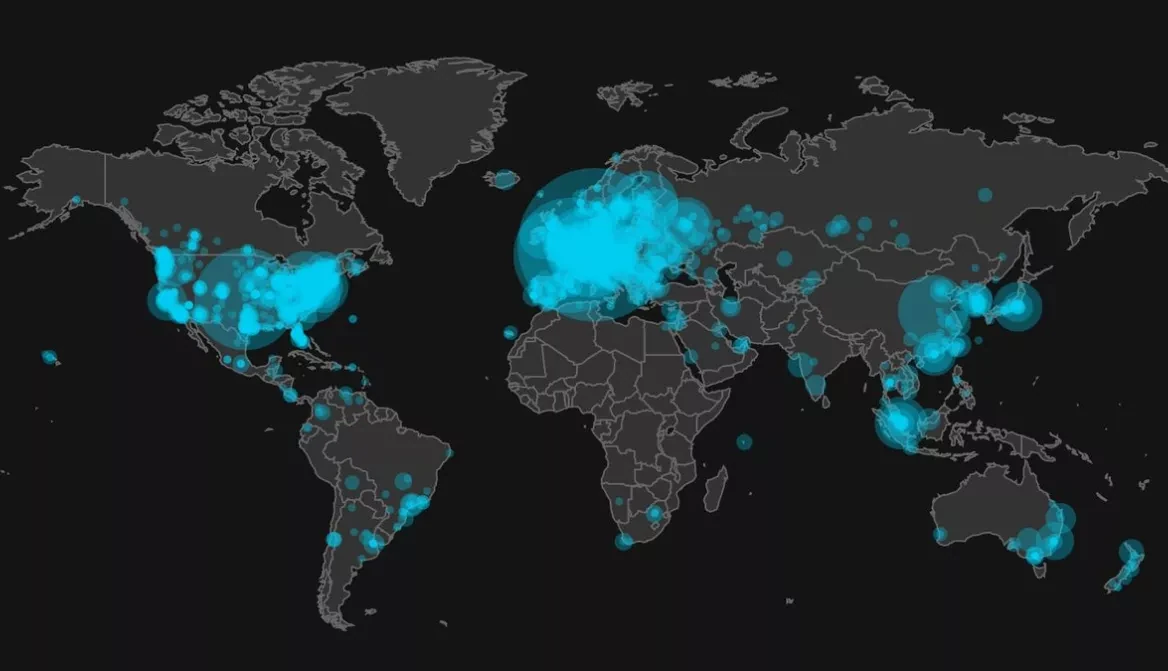
Each node holds a copy of the blockchain, which permits transaction verification and prevents any fraud attempt. The decentralized nature of the network gives Bitcoin exceptional resilience and robustness. In fact, to stop the Bitcoin protocol, all nodes around the world would have to be shut down. As of September 2023 there were approximately 45,000 nodes distributed across the globe.
Nodes are capable of verifying the validity of blocks and transactions because they follow the rules of the Bitcoin consensus. These rules establish the Bitcoin's monetary policy, such as the mining reward amount (which we will discuss in more detail in the next section) and the amount of bitcoin in circulation. In a way, nodes act as the network's legal system since they enforce Bitcoin's rules, keeping the network neutral. Consensus rules hardly vary, if at all, because to make changes, the approval of all nodes is required.
Governance within the protocol is beyond the scope of this basic course, but it's important to note that each user running a Bitcoin node can decide which rules to follow. A user may choose to adhere to different rules (i.e., make modifications to the code), but if these changes invalidate the current consensus rules, that node will no longer be part of the Bitcoin network. Consequently, major modifications are rare and require significant coordination among thousands of participants with diverse ideologies and interests, which forces them to provide updates that are considered 'better' by all Bitcoin users.
What does a node look like?
There are several options available when you want to install your own node, with different maintenance costs. You can simply run the Bitcoin Core software on your computer, but it will require a significant amount of storage space, as the blockchain is about ~500GB. To overcome this constraint, you can choose to only keep the last N blocks in the memory by creating a "pruned node". For this second solution, the cost is negligible because the node is only active when you need it.

A second option is to use a dedicated piece of hardware for this purpose, such as a Raspberry Pi 4 with a sufficiently large SSD (about ~2TB). This other option is more expensive if you have to buy the hardware, but it represents a little less than €10.00 per year in terms of electricity consumption. From a bandwidth perspective, considering 1 block of 1MB every 10 minutes, it corresponds approximately to 5GB per month.
Nodes must remain accessible to everyone!
The affordable cost and accessibility of a Bitcoin node in terms of hardware resources, storage, and bandwidth is a very important characteristic, as it facilitates the decentralization of the network.
Indeed, everyone has a good reason to run a node! The costs and efforts are minimal compared to the benefit obtained. You just have to embark on the adventure and join thousands of other bitcoiners to form the Bitcoin network all together.
On the contrary, if the blocks were 100 times heavier, we could certainly make 100 times more transactions every 10 minutes, but running a Bitcoin node would require a 50TB hard disk, a bandwidth of over 500GB/month, and a piece of hardware capable of validating hundreds of thousands of transactions in less than 10 minutes. In this hypothetical situation with 100 times larger blocks, running a Bitcoin node would not be accessible to the average person, which would compromise both the decentralization of the protocol and the immutability of transactions and consensus rules.
Thus, the protocol constraints have been designed to enable as many people as possible to run their own Bitcoin nodes. In fact, the year 2017 was marked by an intense controversy known as the "block size war". This conflict pitted those who wanted to modify Bitcoin by increasing the block size to enhance transaction capacity (miners, exchange platforms, and institutions) against those who sought to preserve the independence and power of users (nodes and users). In the end, the second party triumphed.
Following this victory, the nodes activated an update called SegWit, paving the way for the implementation of the Lightning Network, an instant Bitcoin payment network built as a second layer of the Bitcoin blockchain. This situation demonstrates that users, through their nodes, hold real power within Bitcoin, allowing them to stand up to large institutions in times of disagreement.
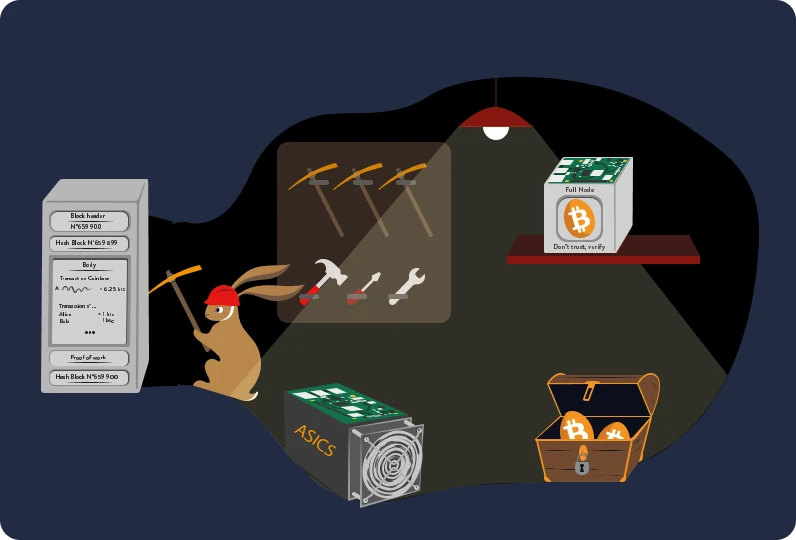
Miners
Miners secure the network and add transactions to the blocks. They use electricity through ASIC machines to solve the Bitcoin proof of work.

Explanation of Proof of Work
"Proof of Work" (POW) is the security consensus mechanism of the Bitcoin protocol. It is the foundation of everything and plays a crucial role in the game theory of Bitcoin.
To explain how it works, envision a universal lottery where everyone can participate. The goal is to find a specific number that enables the winner to sign a valid block, earning a reward in Bitcoin. This number is very simple to verify using the SHA-256 hash function, but difficult to find: participants (miners) will try billions upon billions of possibilities, such as 1, 52, 2648, 26874615, 15344854131318631, and so on, until they discover the right one.
If the chosen number is correct: Jackpot! Otherwise, the search continues. To optimize the number of attempts, they will use specific machines called ASICs, which have the sole role of calculating billions of possibilities per second (the total quantity of attempts is called "HashRate"). To operate these machines, large quantities of electricity must be consumed. Therefore, POW transforms energy into currency, connecting the real world and the digital world to create the first energy-based currency.
The machines operate continuously, and after an average of 10 minutes, a winner emerges: this participant has successfully found the correct hash that falls below the difficulty threshold. This single winner will then sign the new block of the timestamp server, adding it to the blockchain. They receive their rewards and return to try their luck at mining the next block. This process has been ongoing for more than ten years, with a winner confirming Bitcoin transactions every 10 minutes while also securing past transactions, thereby making the Bitcoin blockchain more robust and secure.
Every 2016 blocks (approximately every two weeks), the difficulty adjustment rebalances the global mining game based on the number of participants. This adjustment is necessary because the number of miners and their combined computing power can vary significantly over time. To maintain the target block time, the network recalibrates the difficulty level based on how quickly the last 2016 blocks were mined. If they were mined too quickly, the difficulty increases, making it harder to find the correct hash. On the contrary, if they were mined too slowly, the difficulty decreases, making it easier.

Mining is constantly evolving
Over the years, miners have equipped themselves with increasingly efficient computer hardware to produce as many hashes as possible per second (HashRate) while consuming the least amount of energy in the most cost-effective way possible. The early miners, like Satoshi or Hal Finney, mined using just their CPU, then others started mining with their graphics cards. Nowadays, miners use ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit): machines solely designed to apply the SHA256 algorithm.

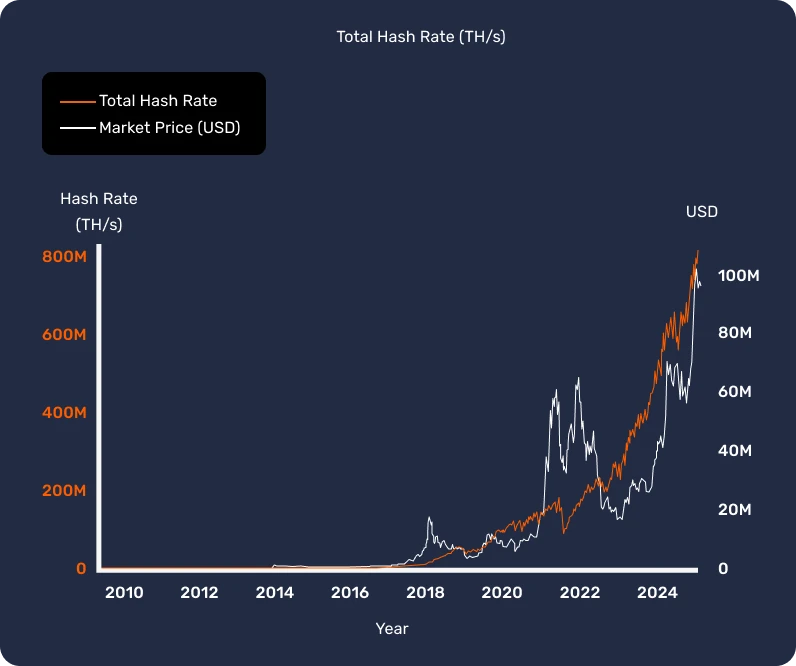
The hashrate of the Bitcoin network represents the number of attempts made per second to find the next block. Today the hashrate surpasses 500 TH/s, which is 500,000 billion attempts per second! The higher the global hashrate, the more difficult it is for a malicious actor to monopolize the resources needed to obtain the majority of the mining power and spend their funds more than once (double spending problem). It is therefore more economically viable to follow the rules of the Bitcoin protocol than to act against them.
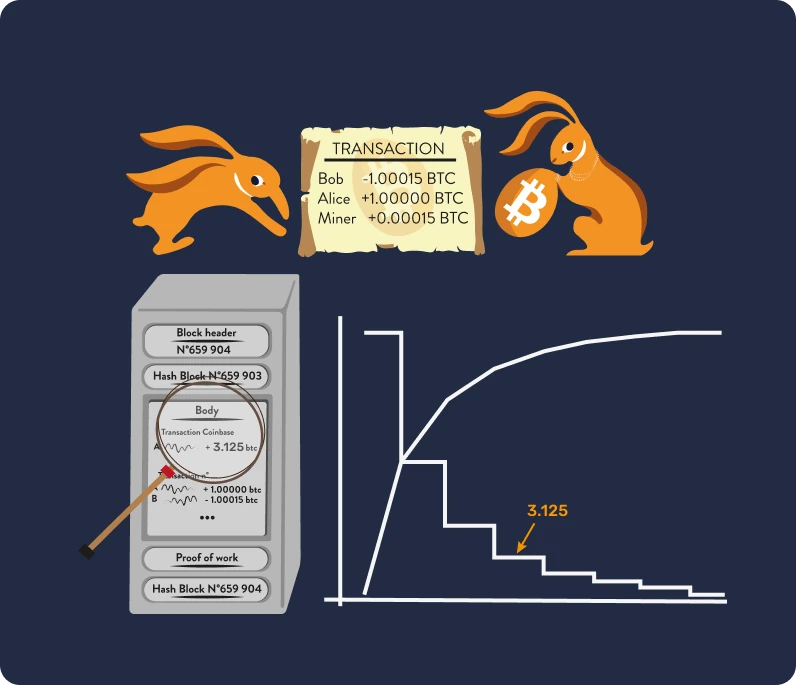
What can be found in a block?
The block header contains several elements such as the time, the difficulty target, the number of the last block, the version used, and the Merkle Root of the previous transactions.
The coinbase transaction is always the first transaction included in a block: it contains the miner's reward for performing proof-of-work. Then come the validated transactions. Miners will choose to insert the transactions which give them the most profit, namely small-sized transactions with maximum fees.
Miner compensation
Initially, a miner is compensated when they find a valid block. More precisely, they are rewarded in two ways:
- through the subsidy (newly minted bitcoins) included in the block;
- through transaction fees from the transactions included in the block.
The amount of the subsidy is defined by the consensus rules and depends on the Epoch: block reward = block subsidy + transaction fees.
For the first blocks, the block subsidy was 50 bitcoins. Every 210,000 blocks (approximately every 4 years), this amount is halved. Today (in 2024), we are in the 5th Epoch, which means that the subsidy is 3.125 bitcoins. In short, this is the automatic mechanism that releases new bitcoins in the system. The subsidy decreases over time, until it meets the limit of issuance of 21 million bitcoins. There are already over 19.4 million bitcoins in circulation, which is over 92%.
The second method of compensation is defined by the amount chosen by users for transaction fees, which show the urgency of the user to have their transaction included in the next block. Since miners want to maximize their income, they will tend to prioritize transactions with high transaction fees.
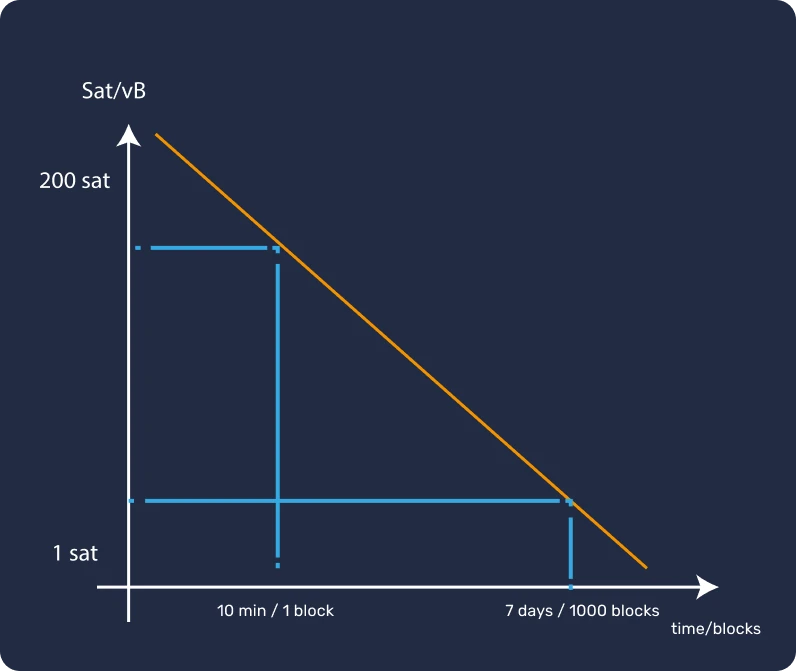
To stabilize their business model, which relies on the rewards they receive for each valid block, miners often create groups through "mining pools", where they pool their computing resources.
Why bother doing all this?
In short, the innovation of Bitcoin is to propose a solution to the problem of double spending through the use of a blockchain based on Proof-of-Work with a floating difficulty. In the digital world, the concept of ownership differs from that of the physical world. In fact, in the digital world, everything can be copied and pasted, which creates the risk of using digital assets of value more than once, or double spending. Trusted intermediaries, such as banks, have been created to solve this technological problem and ensure that when an asset is transferred, it no longer belongs to the sender.
But how can this be done without a trusted intermediary? This problem is well described through the Byzantine Generals paradox, a problem of coordinating information in a system where various actors cannot be trusted. In the Byzantine Generals Problem, a group of generals must coordinate an attack on a city, but some may be traitors trying to disrupt the plan. The challenge is for the loyal generals to reach a consensus on whether to attack or retreat, despite receiving potentially misleading messages from the traitors.
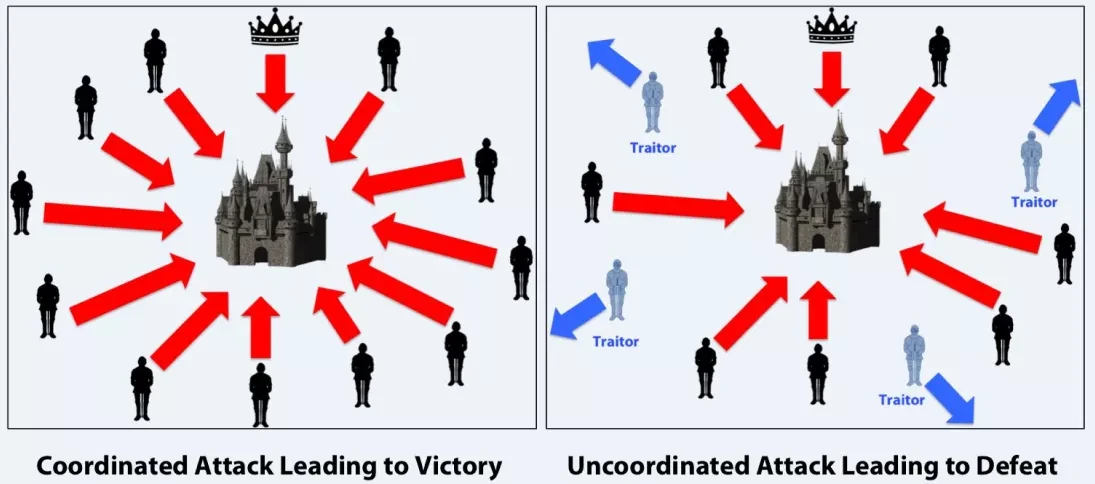
Bitcoin is therefore a kind of solution to this issue, or at least to work around it. The "generals" of Bitcoin, or miners, produce blocks (of information) and Bitcoin nodes verify financial transactions using consensus rules to ensure the authenticity of the information. The asymmetry in the energy cost between information production and verification ensures the reliability of the information, without a trusted third party.
Miners are the builders of the Bitcoin network security. By spending energy to produce hashes, they build a wall that makes it extremely costly for a malicious agent to rewrite the transaction history, and this economic disincentive deters others from behaving dishonestly.
Even in the case of a 51% attack, where an agent would possess more than half of the hashrate, the network would remain secure because the attacker must spend as much energy as all the miners combined to attempt to modify the blockchain. This energy-intensive proof-of-work mechanism is what ensures the network's security.
In summary
The game theory applied to Bitcoin eliminates dishonest miners, who use ASIC machines to mine and receive a reward in case of success. Additionally, they often join mining pools to share their computing power and receive smaller but more regular rewards. While Bitcoin mining incurs high energy costs, it is crucial for the operation and security of the Bitcoin network. The proof-of-work mechanism and blockchain technology address the double-spending problem and ensure the integrity of information without relying on a trusted third party. Although producing information requires significant energy expenditure, verifying that information incurs a negligible cost. This asymmetry reinforces the network's security, making it more economically viable to adhere to consensus rules rather than attempt to break them.
If you want to delve deeper into the specific topic of Bitcoin mining, you can consult our MIN 201 course. You will discover the workings and role of Proof-of-Work, as well as the mechanics of the mining industry. We also explain how to convert an ASIC into a heater, allowing you to mine your first satoshis while heating your home!
https://planb.network/courses/ce272232-0d97-4482-884a-0f77a2ebc036
Bitcoin and Ecology
In the previous section, we understood that the security of the Bitcoin protocol relies on high energy consumption to produce a public ledger of transactions without a trusted third party. In mainstream media, the overall energy cost is often compared to the electricity usage of a small country. But does this comparison make sense? Is it relevant to understand the reasons behind such costs?
The energy costs of Bitcoin.
First, let's qualitatively assess the environmental cost of mining. A miner must have a machine like an ASIC and a source of energy in the form of electricity to power these machines. ASICs are mostly made of aluminum and can be either recycled or reused for a second purpose (as demonstrated by the Attakaï project described in our course MIN201), which transforms an Antminer S9 into a space heater). The main concern is therefore the energy consumption.

The electricity consumption represents almost all of the costs for a miner. Therefore, they are encouraged to find a cheap source of electricity, so they can go to places where power plants are installed but not yet connected to the electrical grid of the territory. In this case, miners act as a last resort buyer, allowing power plants to secure financing even before being connected to the electrical network. When they are connected, the demand for electricity will increase, which will raise the price and make it less profitable for miners to obtain electricity in these places. Since the machines can be easily moved, miners will then decide to take their installation and settle further away where the demand is low and so is the price, most often in areas where they can get energy from green power plants.
An endless debate
Thus, the debate on the ecological impact of Bitcoin is often misguided, mainly due to an insufficient understanding of its usefulness. Bitcoin cannot be evaluated simply in terms of energy costs per transaction, because miners secure both the current and historical network, and transactions are grouped and not all equivalent. Besides, the impact of the Lightning Network is not even taken into account. Those who claim that Bitcoin consumes too much energy may have political motivations or seek to sell their own blockchain solution. Many times, the ecological pretext is used to justify the banning of Bitcoin.
It is important to emphasize that Bitcoin, as a revolutionary invention, provides a means for individuals living under financial oppression or dictatorial regimes to fight for their freedom. As a last resort, Bitcoin offers a pathway to financial independence by circumventing censorship and banking restrictions. More than just a currency, Bitcoin serves as a form of communication and a symbol of freedom, and the energy expended by miners plays a crucial role in defending this freedom, enabling emancipation from a financial system dominated by debt and excessive monetary creation by central banks.



For those living in countries with high inflation rates, Bitcoin is a matter of survival. It provides a means to survive in precarious financial situations. Furthermore, Bitcoin offers a more equitable and impartial financial system, providing billions of people worldwide with access to financial resources. Given this perspective, is the energy consumption justified?
Bitcoin could be a net positive for the environment
Finally, it is essential to discuss the economic and environmental consequences of Bitcoin adoption.
When comparing it to the current financial system, the latter, due to its encouragement of overconsumption and debt, poses serious problems. Factors such as easy access to credit, monetary issuance by banks, and the practice of fractional reserve banking all contribute to over-indebtedness and, as a result, excessive consumption.

It is necessary to reform the monetary system in order to reflect the scarcity of our resources with the scarcity of our currency. This will encourage more responsible consumption and a long-term vision. Conversely, inflation, by encouraging consumption and investment, has a negative long-term impact on the environment.
The current financial system aligns with the ideas of Keynesian economics, which, unlike Austrian economics, does not take into account the temporal and dynamic aspects of situations and resources. In other words, an unlimited currency cannot effectively represent the limited resources of our planet.

Politicians usually have short-term vision and they need economic growth to be reelected, so they are not able to solve ecological problems in the long term. The adoption of a sound currency like Bitcoin is a potential alternative that could empower people economically.
Critics do not acknowledge that Bitcoin promotes the use of green energy. For example, the flames ignited in oil wells sites to burn methane and prevent pollution can be extinguished by Bitcoin miners, because methane can be converted into electricity to power mining machines, which is beneficial for the environment.
Follow one of Bitcoin's maxims: Don't trust, verify for yourself!
Brief summary of the technical features of Bitcoin
Satoshi Nakamoto released the Bitcoin protocol in January 2009, which has since evolved thanks to a growing community of developers, miners, and users with Bitcoin nodes. By keeping their own copy of the Bitcoin blockchain, a public ledger of all Bitcoin transactions, these nodes can ensure the validity of transactions according to Bitcoin's consensus rules. This includes ensuring that miners produce valid blocks, which contain thousands of pending transactions.
On average, a block is created every 10 minutes, and the miner who finds a valid hash for the next block is rewarded by the protocol with both a subsidy amount that is defined by the consensus rules, as well as the transaction fees from all transactions included in the valid block. Since the result of the hashing algorithm (SHA256) for a given input is considered unpredictable, the mining process involves building numerous candidate blocks and testing if their hash is valid or not. However, to ensure that the average time between two blocks remains constant (~10 mins) regardless of the number of miners and their computing power, the difficulty of finding a valid hash adjusts every 2016 blocks, approximately every 2 weeks. Miners have developed specialized SHA256 machines over time, called ASICS, to increase the hash rate per joule, which means the number of attempts per second per consumed energy.
In order for miners to be as profitable as possible in their activity, they must obtain the cheapest electricity possible, which is often in remote locations, within power plants that are not yet connected to the grid. The miner then acts as a buyer of last resort, and, as soon as the price of electricity increases due to an rise in demand, the miner will tend to relocate their activity elsewhere.
Thus, the Bitcoin protocol is an uncensorable and unstoppable monetary system because each component of the protocol is distributed geographically across the globe. For example, there are more than 40,000 Bitcoin nodes across all continents. Bitcoin's consensus rules are such that it is economically more profitable to follow them than to try to break them, and therefore no trust is required between actors. Bitcoin has no leader and cannot be stopped. Even if it is possible to regulate exchange platforms to limit Bitcoin, this approach has a marginal impact on the system. In short, no judge or state can censor or stop Bitcoin.
How do You Obtain Bitcoin?
Bitcoin Never Sleeps!
The price of Bitcoin is often characterized by significant volatility. Its value can fluctuate considerably depending on market variations or on bullish and bearish phases, just like any other financial market.

To put it simply, humans tend to buy everything at once and sell everything at once. Bitcoin is not immune to human nature.
Understanding adoption waves
Both the development and the evolution of Bitcoin are largely linked to the different groups of actors who have gradually integrated its ecosystem.
- The believers:
The early users of Bitcoin were mainly technophiles, cypherpunks, libertarians, and gold enthusiasts. These groups were attracted to it because of its value as trustless electronic cash, its resistance to censorship, and its transparent, immutable monetary policy.
- The dark web & criminals
Then, Bitcoin's use expanded into dark web marketplaces like Silk Road, largely due to its uncontrollable and pseudonymous nature, which also attracted individuals beyond that platform, including some people engaged in criminal activities. However, it's important to emphasize that it is the application of a tool, rather than the tool itself, that determines legality. The illegal use of Bitcoin does not inherently make someone a criminal; rather, it is the specific actions that can be classified as illegal. For instance, using Bitcoin to purchase certain drugs may be legal or illegal depending on the regulations governing the territory where the transaction occurs.
- The ICO frenzy and the arrival of the general public.
The year 2017 was marked by a significant speculative bubble in the cryptocurrency world, especially with the launch of thousands of Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs). However, many of these new cryptocurrencies had no concrete development or utility, and quickly disappeared. This 2017 bubble was followed by a strong correction in 2018-2019.
- The NFT bubble and DeFi
Then again in 2020, the market experienced another speculative bubble that drove the price of Bitcoin to $60,000. This bubble was different from the previous ones because of the broader diversification of investors, including financial institutions and large corporations. However, as with previous bubbles, significant corrections tend to follow once the initial euphoria fades.
Bitcoin and volatility
Based on past cycles, it seems that the periodicity of Bitcoin's economic cycles is equivalent to the duration between two halvings, perhaps because the halving event acts as a trigger by cutting the emission of new bitcoins in half.
These significant fluctuations have earned Bitcoin a reputation as a highly volatile asset, often leading to substantial losses for its users. Although the price can drop by 10%, 20% or even 50% in a few days, it is important to understand that the Bitcoin protocol itself is not affected by price changes.
This significant volatility is fully accepted today by Bitcoin actors and can be mitigated by several solutions such as financial hedges (stablecoins), a strong long-term belief (hodling), or simply avoiding the risk of investing 100% of one’s funds in Bitcoin without a solid understanding. Understanding why the price of Bitcoin fluctuates so much is therefore essential to progress in this industry, as it is ultimately the price movements and cycles that help temper and regulate the market to some extent. However, it is fundamental to note that as Bitcoin grows and matures, volatility becomes less impactful.
Although the btc/dollar pair fluctuates in the short term, bitcoin, due to its limited quantity of 21 million bitcoins and its halving process (halving the monetary creation every 4 years on average), follows a general upward trend in a quasi-mechanical manner. Of course, like any financial asset, bitcoin is subject to economic cycles including periods of euphoria, speculative bubbles, and corrections. This phenomenon is quite common in emerging technologies, where the market is not always rational or efficient.
A unique market
These cycles of speculative bubbles are quite unique in the world, as it is rare for a single asset to experience such a series of bubbles in succession. This phenomenon can be attributed to the fact that Bitcoin is not merely a bubble destined to burst. Rather, it functions as a currency that is actively used around the globe. The Bitcoin protocol stands out for its ability to operate on a global scale, 24/7, which poses significant challenges for financial authorities attempting to regulate it.

Today, Bitcoin continues to survive and grow even more by being integrated more and more into the traditional market, and the introduction of Bitcoin ETFs, clearer regulations, and improved tools for acquisition and storage are all contributing to this positive momentum. Bitcoin has ONCE AGAIN survived its speculative bubble, so maybe it's not just hot air after all!

Obtaining Bitcoins by Working
A parallel economy is developing
Bitcoin can be seen as the tool to create a parallel economy to fiat currencies, because it is possible to sell goods or services and be paid in bitcoin. Transactions can be made directly in Bitcoin, without the need to go through an exchange platform, but simply going from a Bitcoin wallet to another.
The Bitcoin economy exists and is developing in certain regions of the world, like in El Salvador, where Bitcoin has been a legal tender since 2021. All around us there are some individuals, businesses, and organizations that already accept Bitcoin as a means of payment for their products or services.
In addition, an open-source and collaborative project has been launched, BTCMap, to facilitate the use of Bitcoin in everyday transactions. This platform lists all the merchants that accept Bitcoin, as well as the different Bitcoin communities around the world, so you can visit their website to discover the Bitcoin ecosystem around you. Thus, despite the difficulties and the hesitations, there are initiatives like BTCMap that contribute to making the Bitcoin economy more accessible and convenient for everyone.
Why should we accept Bitcoin instead of buying it?
To obtain bitcoins, you can buy them on platforms regulated by organizations such as the AMF (Autorité des Marchés Financiers) in France, or the Securities & Exchange Commission (SEC) in the U.S.A., but this solution entails the traceability of your transactions. Another method to obtain bitcoins is to accept them as a means of payment for the products or services you offer, so you can acquire bitcoins through your work without constantly worrying about the price of Bitcoin.
Furthermore, accepting Bitcoin as a merchant has several advantages, including censorship resistance, reduced transaction fees, increased efficiency, protection against inflation, as well as financial freedom and sovereignty.
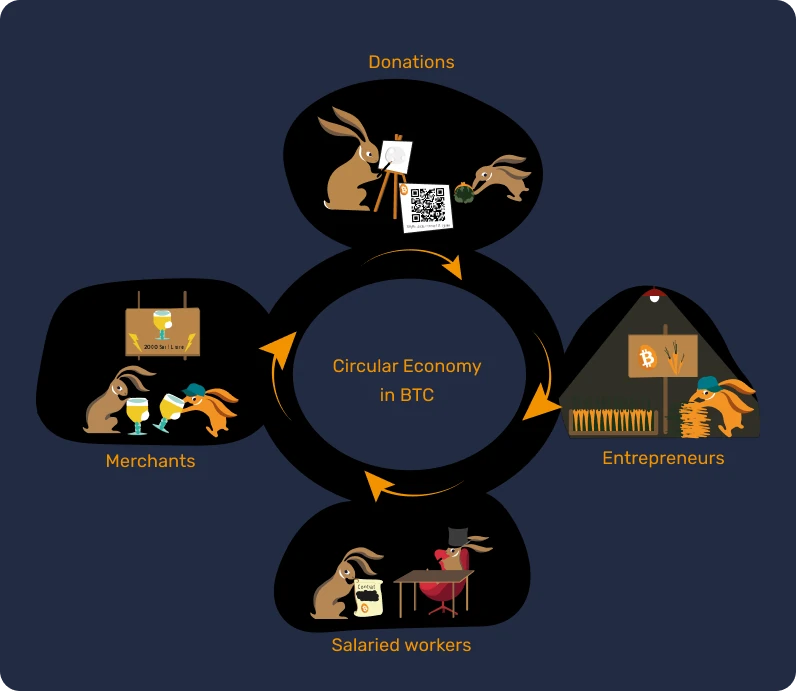
How can you proceed?
To accept Bitcoin, it is necessary to study the different available solutions and choose the one that best suits your business. There is no perfect solution, and several factors must be taken into account to make your choice, such as the expected transaction volume, allocated budget, and type of business (online or physical).
We will cover this topic in detail in another course, but to keep it simple, we can consider several categories of businesses and therefore related solutions.
- Simple online solution: OpenNode
- Solution for amateur merchants: Swiss Bitcoin Pay
- Solution for large organizations or passionate bitcoiners: BTCpay Server
To further explore this topic, we recommend our BIZ101 course! Discover how to effectively integrate bitcoin into your company's treasury, accept bitcoin as a means of payment according to your organization's profile, and understand the related tax and accounting requirements:
https://planb.network/courses/a804c4b6-9ff5-4a29-a530-7d2f5d04bb7a
Saving with Bitcoin
A warning before getting started!
Bitcoin has become a major financial asset, mainly due to its limited supply and increasing demand. However, buying Bitcoin carries risks that require special attention. It is therefore recommended to conduct your own research and learn more about the subject to become familiar with the technology before investing any funds.
- Only invest what you can afford to lose.
- Bitcoin is a highly volatile financial asset, and its price can drop to 0.
- Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance.
- Contact your financial advisor if needed.
Plan ₿ Network does not provide any investment advice, and nothing stated here should be considered as such
Mini Checklist before taking the plunge
Before diving into buying Bitcoin, make sure you have:
- A secure wallet.
- A solid understanding of Bitcoin.
- A savings plan to follow.
- A long-term vision.
If the subject is still unclear, be aware that the BTC102 course will guide you in securing and acquiring your first bitcoins. Here, we will only skim the surface of the topic.
In concrete terms, there are two questions to ask yourself:
- Should you adopt a gradual or an all-at-once acquisition strategy?
- Should you use a regulated or an unregulated platform?
Acquisition strategies
- Dollar Cost Average
This gradual strategy involves recurring purchases, meaning buying small amounts of Bitcoin at regular intervals. This method smooths out the price over time and provides continuous growth in the amount of bitcoin owned. It is an ideal solution for long-term savings, and alleviates the concerns about Bitcoin's price volatility. Once set up, you can simply forget about it and watch your investment grow.

Beware of UTXOs: Remember to consolidate your UTXOs in your wallets from time to time. This practice is essential for effectively managing your bitcoins and avoiding unnecessary fees during transactions.
An UTXO is an output of a transaction that has not yet been spent, meaning it was not used as an input for a new transaction. Consolidating them means combining several small UTXOs into one larger one, in order to decrease the "weight" of the transaction, and thus pay lower fees.
- Spontaneous purchase
An all-at-once solution could be a spontaneous purchase, which is used to immediately gain exposure to bitcoin. Whether it's buying during a crash or taking advantage of a bonus, the decision is yours. You will need to muster up your courage and press the buy-button.
In this case, you should be careful and control your emotions, as the price of bitcoin can be quite volatile. In fact, FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) and FUD (Fear, Uncertainty, Doubt) are your worst enemies! Remember to stay calm and follow the strategy you have established in advance, to avoid impulsive and potentially harmful decision-making.
Who should we buy our bitcoin from?
There are several ways to acquire bitcoins, each subject to its own set of regulations that can vary by jurisdiction. Some platforms require identification for verification (KYC), while others do not. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the regulations associated with each platform.
- DCA platforms
As we introduced above, a common method to accumulate bitcoins is the Dollar Cost Averaging (DCA), which involves regularly buying small amounts. Several platforms offer this service, such as those listed on our dedicated page. In addition to the simplicity of setting up a DCA, withdrawals to your wallet are generally automatic, meaning you will always have control over your assets.
Today, almost all DCA solutions are relatively efficient and have almost similar fees, so the choice will depend more on availability in your country.
- Broker platforms
For large-scale investments, regulated and recognized platforms such as Kraken, Bitstamp, and Paymium are recommended. They offer a safe and secure environment for high-volume transactions.
Their use is simple and accessible to everyone:
- Set up a KYC account
- Transfer funds to your account
- Purchase bitcoin
- Withdraw bitcoin to your wallet
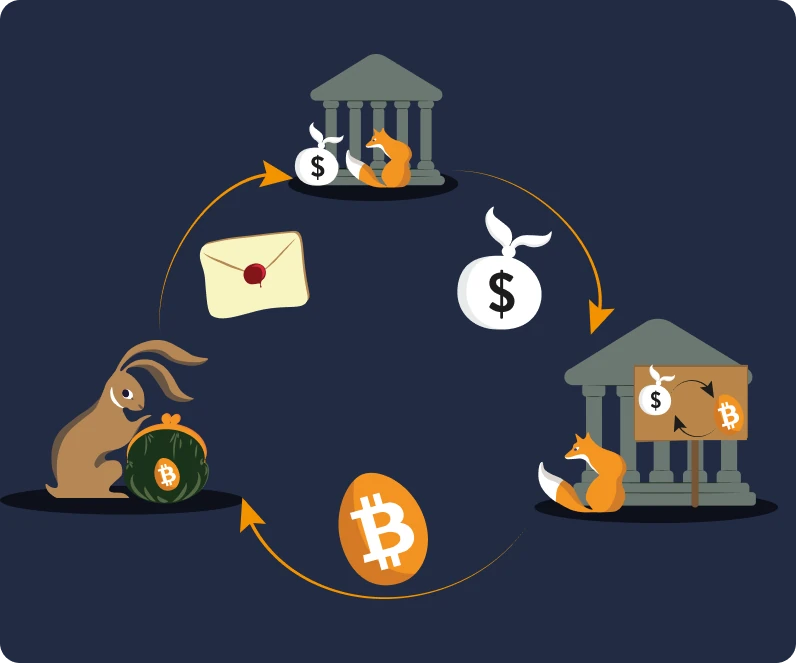
After the purchase, it is advisable to immediately withdraw the bitcoins from the exchange platforms to minimize the risks of hacking and fund blocking. Be aware that withdrawal fees can be high, sometimes up to 25 euros depending on the platform.
Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations require users to provide identification to combat terrorism financing, tax evasion, and money laundering.
It is essential to recognize that KYC is a significant topic of discussion in the Bitcoin industry. While many people debate its effectiveness, there are numerous concerns associated with it. In many of our academy's training programs and content, we advise advanced users to avoid platforms that require KYC, as there are often more privacy-focused alternatives available.
Non-KYC solutions
In addition, there are several marketplaces where to buy and sell bitcoins in a peer-to-peer exchange. In general, you may consider the following:
- Bitcoin ATMs
- Physical meetings with other bitcoin enthusiasts
- Illegal and unregulated platforms
- Peer-to-peer matchmaking solutions
- Neobanks operating in Bitcoin-friendly nations.

Finally, it is important to note that tax obligations may vary depending on the jurisdiction, so we strongly encourage you to consult the regulations in your country before taking any actions that could put you at risk.
Hyper-bitcoinization
The wild race is just beginning!
Like any new technology, the adoption of Bitcoin follows an S-curve, illustrating the progression from early adopters to broader acceptance. We have moved beyond the era of early adopters, and indicators suggest a potential democratization of Bitcoin. After all, it is a viral technology that cannot be easily halted. On the one hand, El Salvador has taken the bold step of fully adopting Bitcoin as legal tender. On the opposite, other countries have responded by banning it and criminalizing its usage, which shows that Bitcoin adoption is complex and is exposed to the influence of cultural, historical, and national factors.

The rise of Bitcoin forces companies, universities, regulators, and individuals to take this new technology into account. New tools need to be created, services need to be adapted, and innovation must continue to ensure their survival. This context raises many questions related to various fields, including cryptography, game theory, economics and monetary policy, computer science, philosophy, energy, laws, and regulation. In short, Bitcoin is a multidisciplinary subject.

Bitcoin is a 0 to 1
In the end, we invite you to reflect on this new monetary revolution. There is so much to explore with Bitcoin that it is complicated to assimilate everything at once. Take your time, Bitcoin is not going to disappear. On the contrary, the revolution has just begun. We believe we are capable of creating the world we want to entrust to our children: a world where human sovereignty is a right, where privacy is respected by default, and where money is not manipulated. We hope that, together, we will achieve this.
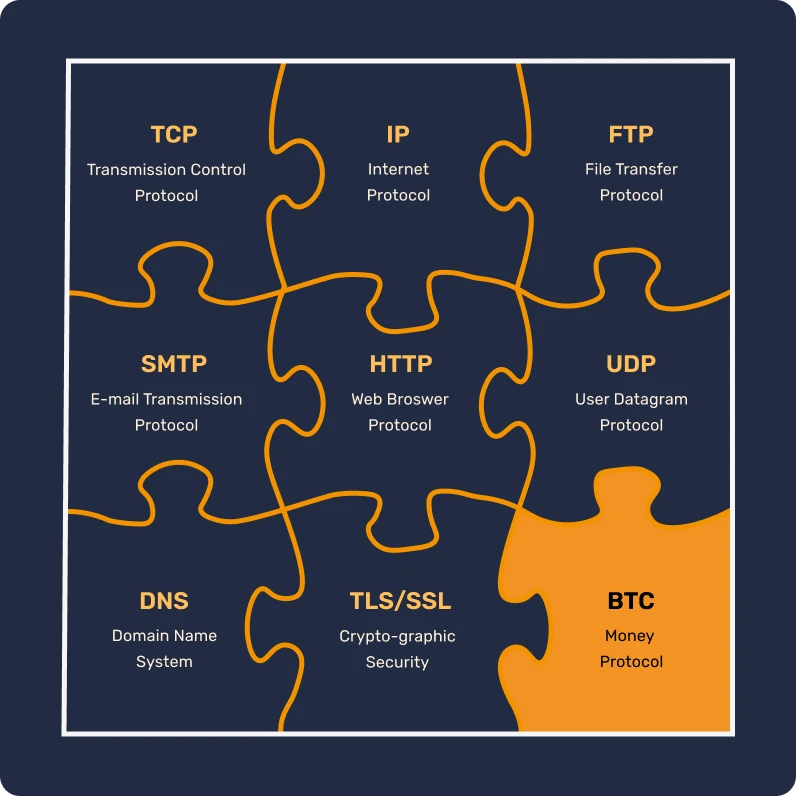
If you want to broaden your knowledge about Bitcoin, this is the right time: a large number of authors, thinkers, and essayists have created educational content about Bitcoin. For the past few years, we have been listing and categorizing these works to offer a library of resources to the most curious among you. In that section, You will find the best podcasts, websites, articles, tutorials, books, and other content.
"I think that the Internet is going to be one of the major forces for reducing the role of government. The one thing that's missing, but that will soon be developed, is a reliable e-cash - a method whereby on the Internet you can transfer funds from A to B without A knowing B or B knowing A." - Milton Friedman prediction in 1999
The Future of Bitcoin: The Lightning Network
A Brief Introduction to the Lightning Network
Now that we have the basics of the Bitcoin protocol, we will introduce a payment network that uses the Bitcoin protocol to enable lightning-fast transactions: the Lightning Network!
Be aware that the following is only a general description, so, if you want to understand it in deeper details, we invite you to take our LNP201 course.
In a nutshell
The Lightning Network is a revolutionary technology that has profoundly changed our perception of Bitcoin, as it addresses the scalability issue of Bitcoin.
To fully grasp the Lightning Network, it is crucial to understand how Bitcoin evolves and develops in infrastructure layers: the first layer is the blockchain, and the second one is the Lightning Network.
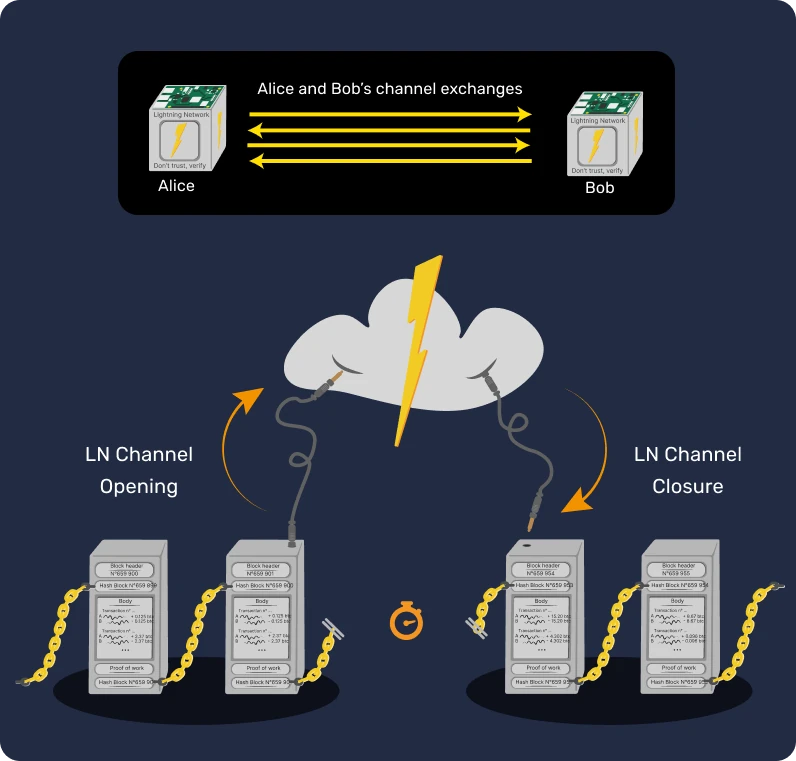
A Blockchain cannot grow indefinitely
The Lightning Network was validated and implemented in 2017 to solve the scalability problem of Bitcoin, as it allows for instant, low-cost Bitcoin transactions.
The scalability problem refers to the challenge of implementing a monetary system capable of providing an ever-increasing number of transactions per second in response to increasing adoption. This issue relates to the blockchain trilemma. Imagine a triangle with decentralization, security, and scalability as its vertices.
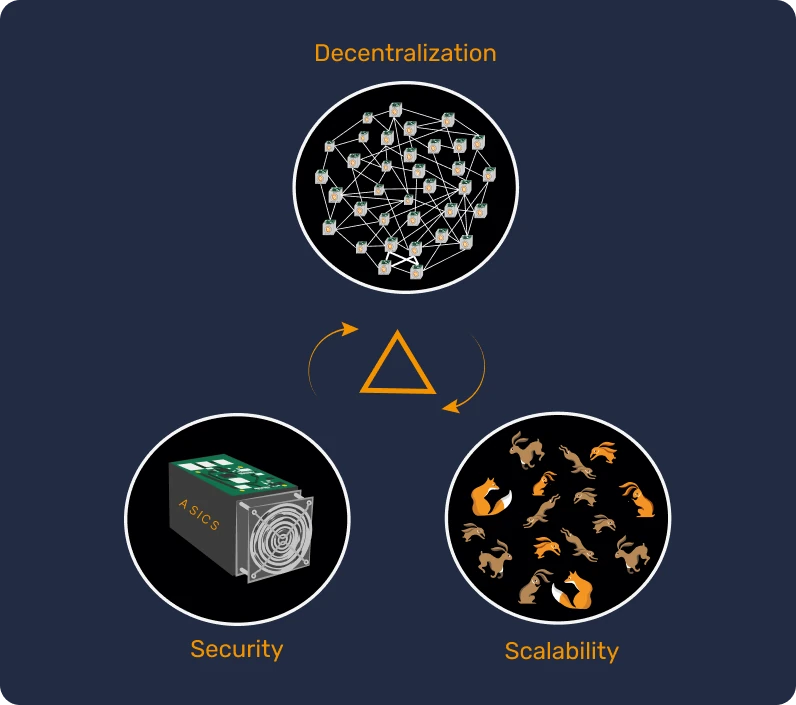
According to it, a protocol based on a blockchain can only satisfy two out of these three features. Within the Bitcoin protocol, developers have made choices to favor decentralization and security. On the one hand, the block size of 1MB and the time between two blocks (on average 10 minutes) allow for running a Bitcoin node at a lower cost, favoring decentralization. On the other hand, the production of blocks through Proof-of-Work makes fraud within the protocol extremely costly, while facilitating verification by network nodes and favoring security. However, these choices impose a limit on the average number of transactions in a block, roughly corresponding to a few transactions per second. This number is ridiculous when compared to the computational capacity of payment processors like VISA (1700/s), but this limit is necessary in order to transact with Bitcoin in a censorship-resistant and trustless manner. Nevertheless, those developing on Bitcoin have been thinking about this problem since the beginning.
Lightning as a layer on top
After years of consideration and multiple attempts, the Lightning protocol emerged. Using a certain number of specifications, this protocol constructs a peer-to-peer payment network by leveraging the security and programmability of Bitcoin's transaction protocol. The Lightning Network acts as a network of payment channels, enabling instant transactions with low fees for the sender, and it even creates exchange routes between individuals who do not have a direct channel connection.
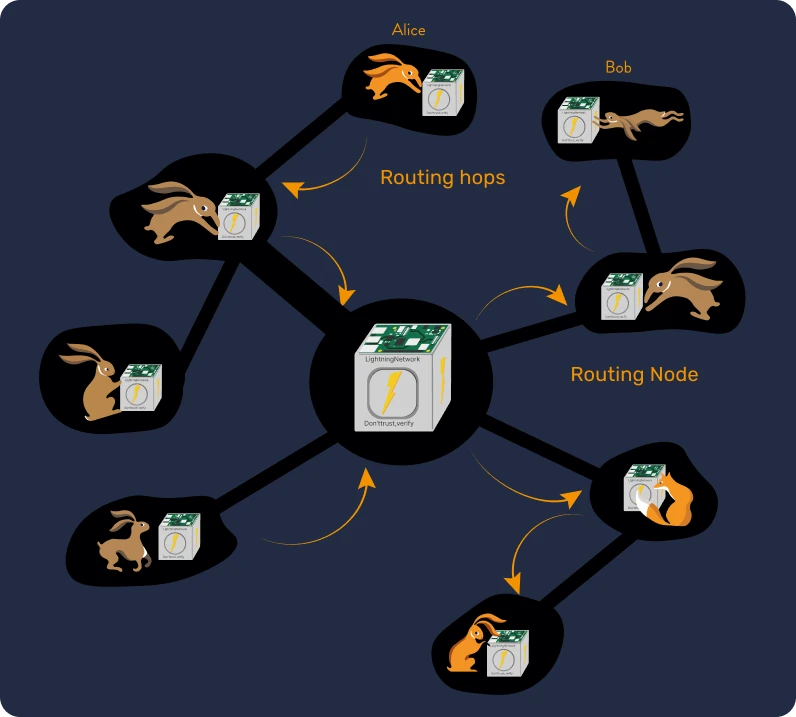
Traditional money transfer services such as Western Union, central banks, Visa, and Mastercard could disappear if they do not adopt the Lightning Network technology, which is more efficient and cost-effective than current payment systems. In fact, the Lightning Network enables nearly unlimited transactions between two peers sharing a channel, incurring only the energy costs associated with the transaction to announce the creation of the channel, rather than on each individual transaction.
Transactions are secured through cryptography and indirectly through the energy consumed by miners on Bitcoin. They can be made instantly, without geographical limitations, with extremely low fees (often less than 0.5%).
In summary, the Lightning Network is a promising attempt to deploy an efficient payment system to buy and sell in Bitcoin. There are already numerous Lightning wallets available, which you can discover in our tutorial section or through our Lightning Network courses.
If you want to go beyond this introduction and understand all the workings of the Lightning Network, we recommend taking this excellent course by Fanis Michalakis on the subject:
https://planb.network/courses/34bd43ef-6683-4a5c-b239-7cb1e40a4aeb
Lightning Network Use Cases
As we have just seen, the Bitcoin protocol, although revolutionary, faces significant challenges in terms of the scalability needed to handle all of our daily transactions. To solve these problems, the Lightning Network was proposed and has since developed into several different implementations, all of which are interoperable:
- Core-lightning by Blockstream
- Eclair by Acinq
- LND by Lightning strike
This peer-to-peer network aims to facilitate micro-transactions (with very low value) that would otherwise be impractical due to high fees and long confirmation times on the Bitcoin blockchain.
What are the use cases of the network?
This technology opens the door to a wide range of potential applications for Bitcoin that were previously out of reach because of the necessary constraints to ensure the security and decentralization of Bitcoin. Among these everyday use cases, we can mention instant billing in both physical and online commerce, streaming money for real-time payments, and micro-donations for content creators. By enabling a network of nearly instant, secure, and low-cost transactions (averaging less than 0.5%), many previously unimaginable business models can be realized. This is made possible because the Lightning Network operates using satoshis (sats), the smallest unit of Bitcoin.

The video game industry offers a particularly interesting example of how the Lightning Network can be used to transform existing business models. The concept of "skin in the game" is an idea that has recently gained popularity in this context. It essentially involves having a financial stake in the outcome of a game. In fact, the Lightning Network allows players to wager very small amounts of money when playing games, such as a few satoshis (about a fraction of a euro cent) to establish a stake that stimulates competition while significantly increasing the cost of using bots.
In summary, the future of micro-transactions with Bitcoin looks promising thanks to innovations like Lightning Network. As these technologies continue to develop and mature, we can expect to see new and exciting applications emerge in the near future.

Another example could be "money streaming": through the Lightning Network, we can make micro-transactions every minute (potentially without a trusted third party), which opens the door to experimenting with economic models where consumers pay for content based on their actual consumption. It is even conceivable to use this system for renting goods. In such a system, money is automatically divided, based on a predefined percentage, among the different contributors to a service or product. This could revolutionize the way we think about payment models: instead of paying a monthly subscription for a service, users could be charged per minute, or even per second, for the time they spend using the service. Such an economic model could have profound implications for content creators, who would be incentivized to produce quality content to keep users' attention.
In conclusion, the Lightning Network opens up a multitude of exciting use cases for Bitcoin users. The resulting economic models and business opportunities are numerous and varied, and we encourage you to check for yourself by trying the podcast application Fountain, which allows you to be rewarded with a few sats for listening to your favorite podcasts!
Red Pill or Blue Pill?
As Morpheus said to Neo: "You take the blue pill, the story ends, you wake up in your bed, and you believe whatever you want to believe. You take the red pill, you stay in Wonderland, and I show you how deep the rabbit hole goes." Are you ready to explore the rabbit hole of Bitcoin? Be careful, as you might rediscover your financial freedom!
Technological future and its implications
Technology is evolving exponentially, and no one can predict its future developments with certainty. World connectivity and artificial intelligence continue to advance, and the knowledge that an individual can acquire through the internet is becoming increasingly immeasurable over time.
If we take AI as an example, these technologies have already surpassed or are approaching human-level performance in a growing number of domains, such as video games, image and text production, and data analysis. One potential implication is that over 80% of jobs will disappear due to AI and automation. As a consequence, several options are available to us, such as restraining technological progress or harnessing the increased capital from productivity gains created by AI.
We have some essential questions to ask ourselves:
How do we manage a society where 80% of jobs will disappear?
How do we revitalize a population?
Is there a need for as many teachers?
The geopolitical, political, and human consequences of automation are not sufficiently discussed. Computing, the internet, streaming, and VR will change education. We could have a universal course for all French students managed by the government and teachers who no longer give lectures but directly accompany the students. Children could go into a virtual world and be accompanied in learning history.
Where is the boundary between a teacher and an AI personification?
How can we guarantee a society that lives in prosperity?
These fundamental questions for our future must be debated and collectively decided. What is the connection with Bitcoin? Just as the Internet revolutionized modes of communication, Bitcoin represents a technological revolution for new forms of large-scale organization, enabling us to exchange value without relying on any trusted third party. Do we want to hinder the technological evolution of the monetary system, or do we wish to embrace the potential for increased capital through the tenfold productivity gains offered by using Bitcoin and Lightning protocols?
What is the future of finance?
These considerations also raise questions about who should hold, authorize, and trace the money we use. The goal is to decide between a closed system with unelected leaders or an open system without trusted third parties, where neutrality prevails.
- Is currency a form of private property?
- Can protesters' accounts be blocked without a Supreme Court order?
- Who guarantees the financial system?
- How can an individual be sovereign over their money and rely on a trusted third party?
- Can money be sent to the other side of the world without fees or intermediaries?
Accepting these new technologies could generate massive economies of scale worldwide. Should we allow the free movement of capital flows? International blockades have economic and political consequences. Is it ethical to use financial intermediaries like Western Union, which sometimes charge up to 25% in fees? We believe that in an increasingly digital world, money should be democratized and considered a common good belonging to the people rather than to the state or to opaque financial institutions.
The question of who should control the banking system is crucial because the rules of the banking game are not transparent and understandable to all, allowing a caste of politicians and regulators to maintain their grip on the system, so it is important to question whether the free market or a group of intellectuals should have the power over it.
Our freedom is at stake.
Censorship must also be questioned: who has the knowledge to decide what should be censored or not? The media has changed their position on certain information and those who were censored before are no longer censored today.
- Who decides what is censorship or propaganda?
- Who has the divine hand over our system?
We strongly believe that tolerating censorship can destroy freedom of expression and the right to assembly, as it can have a negative impact on innovation and free will. Imposing censorship is technically difficult without creating a complete dystopia. Thus, which entity should have the power of censorship? The matter is complicated, and it is also difficult to decide who should be restricted or not.
There are 2.4 billion people in the world without a bank account, which necessarily creates geographical inequalities. On the other hand, Bitcoin grants transactions equality, disregarding your social status or political position. The protocol is apolitical and does not grant specific privileges to leaders or other influential figures, ensuring that everyone has the same opportunities to drive development forward, rather than allowing a few to remain at the top while others are left behind. Should everyone have access to the same currency, regardless of their social status? It is essential to consider the world we want to leave to our children, and we aspire to create an open world where they are free to manage their money as they choose.
Bitcoin is important and should not be considered just a game of chance, so it is crucial to keep asking questions about Bitcoin and its consequences on the world.
Bitcoin: a revolutionary protocol
As we have seen in the previous chapter, the Bitcoin protocol is neutral towards all its users. Thanks to consensus rules and cryptography, we can immutably record transactions in a global public ledger, guaranteeing monetary value transfers without any trusted third party. The second-layer infrastructure (and soon the third layer, with RGB, or "Really Good Bitcoin") is used for network scalability and the development of new functionalities.
Bitcoin has all the necessary characteristics to be an efficient and healthy currency: divisible, instantly transportable, uncensorable, negligible verification costs, and with a monetary policy already set to 21 million units for centuries to come. Bitcoin is pseudonymous and can be exchanged anywhere in the world without any authorization from any entity. You just need to hold your own private keys and remember the saying "Not your keys, not your bitcoins".
It is adopted by diverse groups of people, from cryptographers, to libertarians, to traditional businesses, and even entire countries. However, Bitcoin is for everyone, and as the number of users is growing, so does the number of Bitcoin nodes that serve as guardians of transaction history, ensuring its decentralization.
Bitcoin cannot be stopped and cannot be censored anymore. It is a peaceful revolution that changes the monetary system and enables financial inclusivity. Users can obtain bitcoins by accepting them for their trade or by buying them through regulated or unregulated platforms. They can store funds in their wallets, mobile applications, or physical devices, without the need of trusted intermediaries. Bitcoin advocates transparency, freedom, and individual responsibility: as the saying goes "Don't Trust, Verify".
Satoshi created Bitcoin in 2008 to propose a change to the financial system by redesigning currency. He viewed easy-to-create fiat as a corruption risk - governments can and do abuse it. Bitcoin is a neutral alternative, emancipating us from banks and sparking a peaceful revolution in how we view money.
Are you ready to join?
Final Section
Reviews & Ratings
585729e2-b0ab-51b5-89ec-593e3ea22c57 true
Final Exam
8410e961-3841-5abf-a51d-04fc0139dd59 true
Conclusion
dfc534be-44a9-5e8c-9c98-e51ef0554e91 true